Table of contents
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is forcing a critical decision upon enterprise data leaders. As the new standard for connecting AI agents to business data, MCP has prompted major BI vendors to release their own server implementations. However, the architectural choices behind these servers reveal fundamentally different philosophies about how AI should interact with your data.
On one side, you have Microsoft’s Power BI MCP, a dual-server solution designed for rigorous enterprise governance. On the other, Databox MCP, a unified server designed to enable agile, headless BI workflows.
This guide compares these two approaches to help you decide which architecture best supports your organization’s goal of building a scalable, efficient source of truth for your AI agents.
Defining the Contenders
Before diving into the architecture, it is helpful to clearly define what each solution offers to the AI ecosystem.
What is Power BI MCP?
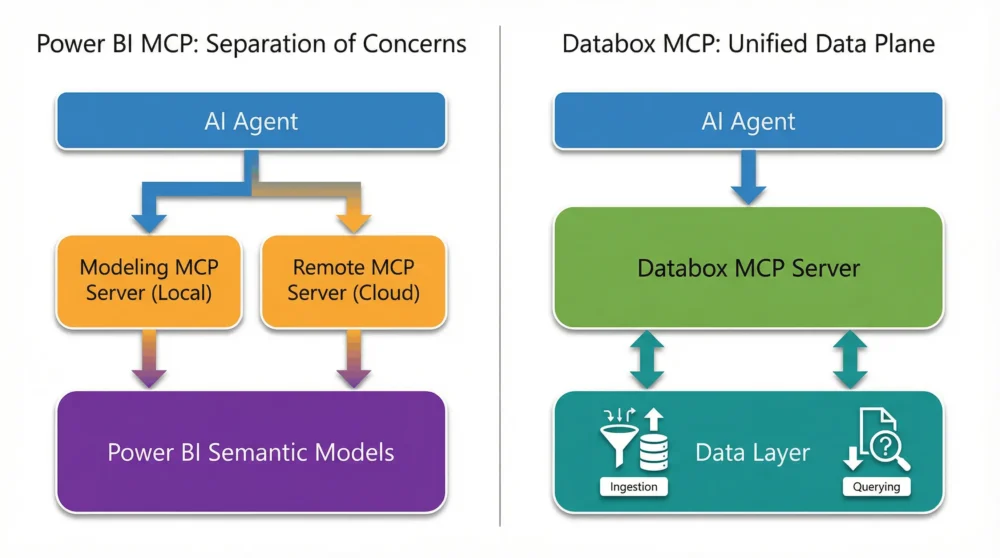
Power BI’s implementation of the Model Context Protocol is a dual-server system built to layer AI capabilities on top of Microsoft’s existing stack. It separates duties into two distinct tools:
- A Local Modeling Server: For developers to build and structure data models.
- A Remote Query Server: For agents and analysts to read data from published reports.
What is Databox MCP?
Databox MCP is a unified server implementation for the Databox Modern BI platform. Unlike Power BI’s split approach, it exposes a single endpoint that allows AI agents to handle the complete data lifecycle—ingesting, managing, and querying data—within one consistent environment. This architecture enables “headless” BI strategies where data is decoupled from specific visualizations.
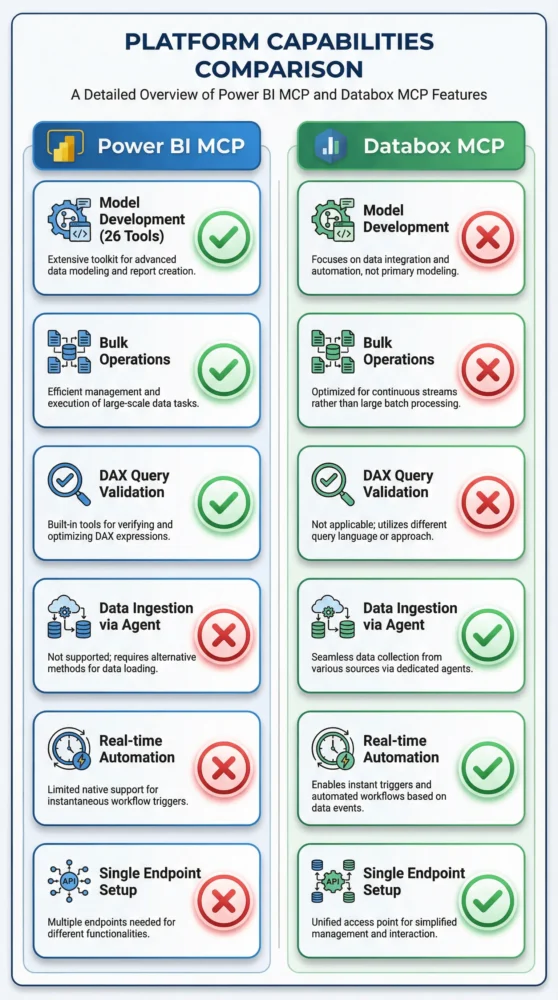
At a Glance Comparison
The following table outlines the structural and functional differences between the two implementations.
| Feature | Power BI Modeling MCP | Power BI Remote MCP | Databox MCP |
| Primary Role | Model Development | Data Querying | Ingestion, Mgmt & Querying |
| Target User | BI Developers | Analysts / End-Users | Data Engineers / AIOps Teams |
| Architectural Philosophy | Separation of Concerns | Governed Access | Unified Data Plane |
| Agent Capabilities | Edit Schema / DAX | Read-Only (Query) | Read & Write (Ingest + Query) |
| Tool Count | 26 (Modeling focus) | 3 (Query focus) | 10 (Full Lifecycle focus) |
| Data Ingestion | No (External Pipelines) | No (Read-Only) | Yes (Direct via Agent) |
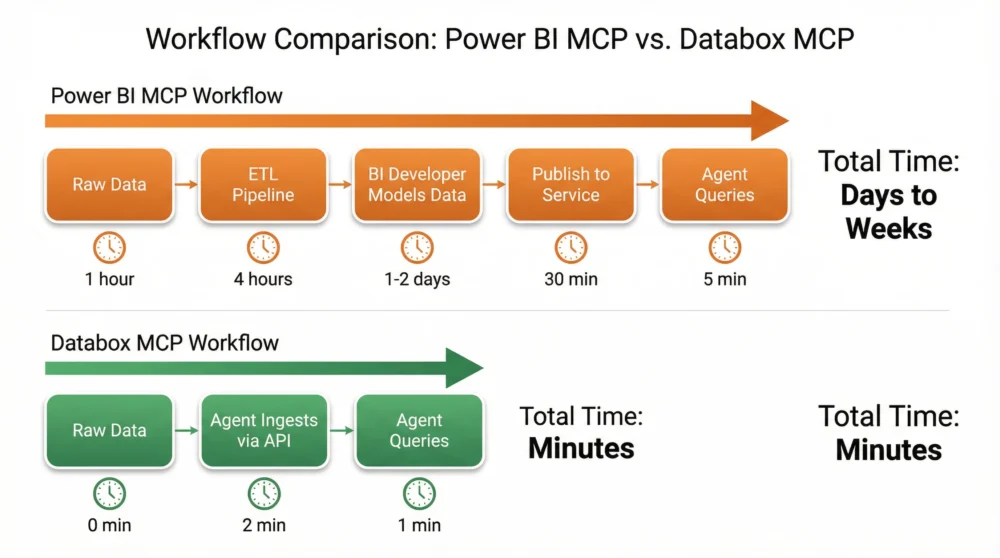
| Setup Complexity | High (Local Install) | Medium (Admin Config) | Low (<60 Seconds) |
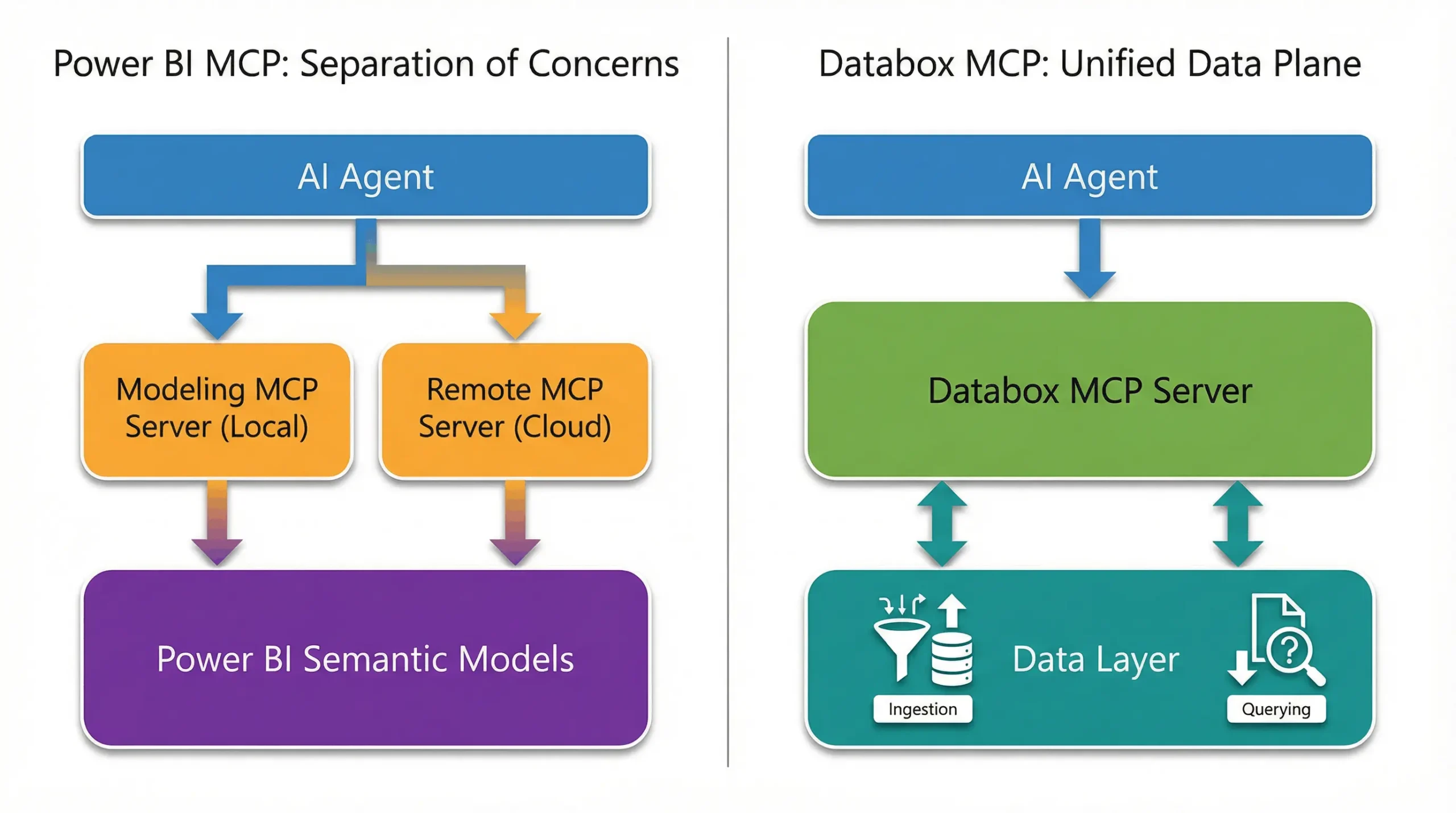
Power BI MCP: Microsoft’s Functional Split
Microsoft’s strategy prioritizes safety and scale. By splitting functionality into two separate servers, they create a firewall between high-risk development tasks and lower-risk analysis.
1. The Developer’s Toolkit (Modeling Server)
This local server is a heavyweight codebase manipulator. With 26 distinct functions, it allows AI agents to perform complex bulk operations, such as creating tables, defining measures with DAX, and applying consistent documentation across a model. It turns the Power BI semantic model into a codebase that an agent can help maintain.
2. The Analyst’s Window (Remote Server)
This cloud-hosted endpoint is strictly for consumption. It leverages the Semantic Link engine to allow agents (like GitHub Copilot) to query data using natural language. Crucially, it is read-only. It enforces existing row-level security and prevents agents from accidentally altering the underlying data model.
The Logic: This split prevents an AI hallucination from breaking a dashboard used by thousands of employees. It is a necessary safety mechanism for massive, static enterprise deployments.
Databox MCP: Agent Centric AI Analytics
While Microsoft separates the ability to change data from the ability to query it, Databox unifies these actions. Databox supports an architecture where the AI agent is not just an observer, but an active participant in data management.
The “Ingest & Query” Advantage
The Databox MCP server provides a focused set of 10 functions that cover the full data lifecycle. The critical differentiator is the ability to ingest data directly.
In the Power BI ecosystem, data ingestion relies on external pipelines (like Fabric or Dataflows) that exist outside the MCP protocol. An AI agent cannot push new data into the system via the MCP server.
In contrast, Databox allows an agent to use ingest_data to push records and immediately use query_dataset_with_ai to analyze them. This creates a closed-loop system where agents can monitor, update, and analyze data in real-time without context switching.
Enabling True AIOps
This unified approach is essential for AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations). Consider an automated workflow:
- Monitor: An agent checks Google Ads spend every hour.
- Detect: It notices CPA spikes by 20%.
- Act: It pauses the campaign and logs the event back into a Databox control dataset for future reporting.
With Power BI’s Remote MCP, the agent can see the spike, but it cannot write the log entry or update the dataset within the same protocol. It is stuck in “read-only” mode. Databox enables the agent to close the loop.
The Verdict: Who Should Choose What?
The choice between Power BI and Databox comes down to your organizational priorities: Governance vs. Agility.
Choose Power BI MCP if:
- You are deeply entrenched in the Microsoft ecosystem: Your data already lives in Fabric, and your teams live in Power BI Desktop.
- Governance is your primary constraint: You need strict separation between model developers and data consumers to comply with enterprise security policies.
- You have a dedicated BI team: You have resources allocated specifically to managing and deploying semantic models.
Choose Databox MCP if:
- You need speed and agility: You want to spin up AI-accessible datasets in minutes, not days.
- You are building AIOps or Automation: You need agents that can both read from and write to your data sources to trigger automated workflows.
- You want to enable Headless BI: You want to decouple your data from specific visualizations, allowing AI agents to access metric performance without navigating complex dashboard structures.
Conclusion
Power BI MCP is an impressive feat of engineering that brings AI connectivity to the traditional, governed enterprise stack. It is the safe choice for stability at scale.
However, for teams that view data as a dynamic asset where speed, flexibility, and automation are important. For those, Databox offers a more streamlined path. By enabling a unified architecture where ingestion and analysis happen side-by-side, Databox allows you to build a modern, responsive data operation that moves as fast as your AI agents do.
Skip the complex setup and get straight to the answers. Try Databox for free to experience true AI-powered business analytics. Connect your sources in seconds and use our analytics MCP to chat with your data inside Claude, Cursor, and more.
Explore Other MCP Comparisons
See how Databox MCP stacks up against other platforms:
Windsor.ai MCP vs. Databox MCP
Supermetrics MCP vs. Databox MCP
Appendix: Complete Function Lists
Power BI Modeling MCP Functions
| Function | Purpose |
| list_tables | Lists all tables in the semantic model |
| get_table | Retrieves detailed information about a specific table |
| create_table | Creates a new table in the model |
| update_table | Updates properties of an existing table |
| delete_table | Deletes a table from the model |
| list_columns | Lists all columns for a specific table |
| get_column | Retrieves detailed information about a specific column |
| create_column | Creates a new column in a table |
| update_column | Updates properties of an existing column |
| delete_column | Deletes a column from a table |
| list_measures | Lists all measures in the model |
| get_measure | Retrieves detailed information about a specific measure |
| create_measure | Creates a new DAX measure |
| update_measure | Updates the expression or properties of a measure |
| delete_measure | Deletes a measure from the model |
| list_relationships | Lists all relationships in the model |
| get_relationship | Retrieves detailed information about a specific relationship |
| create_relationship | Creates a new relationship between tables |
| delete_relationship | Deletes a relationship |
| list_perspectives | Lists all perspectives in the model |
| get_perspective | Retrieves detailed information about a specific perspective |
| create_perspective | Creates a new perspective |
| update_perspective | Updates an existing perspective |
| delete_perspective | Deletes a perspective |
| list_roles | Lists all security roles in the model |
| get_role | Retrieves detailed information about a specific role |
Remote Power BI MCP Functions
| Function | Purpose |
| list_semantic_models | Lists all semantic models accessible to the user |
| get_semantic_model | Retrieves metadata for a specific semantic model |
| query_semantic_model | Executes a DAX query against a semantic model |
Databox MCP Functions
| Function | Purpose |
|---|---|
list_accounts | Lists all Databox accounts accessible to the authenticated user |
list_data_sources | Lists all data sources for a specific account |
create_data_source | Creates a new data source container for organizing datasets |
delete_data_source | Permanently deletes a data source and all its datasets |
list_data_source_datasets | Lists all datasets within a specific data source |
create_dataset | Creates a new dataset with a defined schema (columns, data types) |
delete_dataset | Permanently deletes a dataset and all its data |
ingest_data | Pushes data records into an existing dataset (max 100 records per request) |
get_dataset_ingestions | Retrieves ingestion history for a dataset (job statuses, timestamps, errors) |
query_dataset_with_ai | Queries a dataset using natural language; AI generates SQL and returns insights |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is an MCP Server?
An MCP Server is software that acts as a bridge between an AI model (like Claude) and a data source. It exposes specific tools via the Model Context Protocol standard, allowing the AI to ask questions and retrieve data safely.
Q: Does Databox replace my data warehouse?
No. Databox acts as a modern aggregation layer. While it enables headless BI workflows, it often sits on top of data warehouses or disparate SaaS tools to provide a unified metric view for AI agents.
Q: Can I connect a Postgres database to Databox?
Yes. You can ingest data from virtually any source, including SQL databases like Postgres, into Databox. Once ingested, Databox serves as the central, AI-ready hub for that data.
Q: What are popular MCP Clients?
Common clients include Anthropic’s Claude (Desktop/Web), Cursor (AI code editor), and automation platforms like n8n.
References
1] [Overview of the Power BI MCP servers (Preview) | Microsoft Learn