Table of contents
What kind of content matters to your audience? How are they finding your website? Are there any technical SEO issues that you should see to?
Using Google Search Console can answer all of this and more (so much more).
It’s one of the most robust SEO tools in the industry, and it’s completely free.
Which begs the question – why does it fly under the radar for so many online businesses?
One of the potential reasons why so many marketers overlook the importance of Google Search Console for SEO might be due to its non-intuitive interface and overall complexity.
But that’s still not a good excuse to miss out on some potentially rank-changing insights that can significantly improve the visibility of your business.
In this article, we will Google Search Consolidate your knowledge of this amazing tool, cover all the basics, and show you how to use it.
After that, we’ll present insights from 100+ experts who shared the unique ways they use Google Search Console to increase traffic and rankings.
- What is Google Search Console?
- Why is Google Search Console Important for SEO?
- Get Started with Google Search Console
- Understanding Google Search Console Features and Reports
- How to Use Google Search Console for SEO
- Automate SEO Reporting with Databox
What is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free Google tool that helps you stay on top of your website’s SEO performance, diagnose technical SEO issues, improve rankings, and maintain your site’s digital presence.
The tool provides the most cutting-edge, real-time SEO data available, making it an indispensable ingredient in your SEO stew.
From search performance and user experience-related metrics to discovering security issues, it’s a bit absurd that Google Search Console doesn’t cost a dime.
Startup companies or marketers that are just beginning to learn about optimization and SEO, in general, can rely on Google Search Console as their all-in-one SEO tool.
Why is Google Search Console Important for SEO?
Google Search Console does by far the best job of communicating relevant data between Google and SEO managers.
It offers certain features and information for improving SEO performance that no other SEO tool in the industry can compete with – both technical and content-wise.
Here is how to use Google Search Console to improve SEO:
- Monitor organic traffic, keyword ranking, CTR (click-through rate), average position, traffic data, etc.
- Track index coverage and check whether web pages are properly indexed by Google crawlers.
- Identify removals, disavow files, and sitemaps.
- Make sure page experience, and Core Web Vitals are performing properly.
- Troubleshoot and identify mobile usability issues.
- Check out which manual actions and security issues Google marked
- Analyze crucial backlink data (internal links, external links, top linking sites and pages, and anchor text allocation).
All of this helps you stay on top of your SEO performance, identify any issues, and improve it.
Get Started with Google Search Console
Getting started with Google Search Console can be a bit complicated, which is one of the main reasons why so many SEOs hesitate to use it.
That’s why we’ve broken down the entire process into several segments that you should be able to follow with ease.
Here’s how to get started with Google Search Console.
- Open an Account
- Verify Site Ownership
- Add a Sitemap to Google Search Console
- Add a User to Google Search Console
Set Up a Google Search Console Account
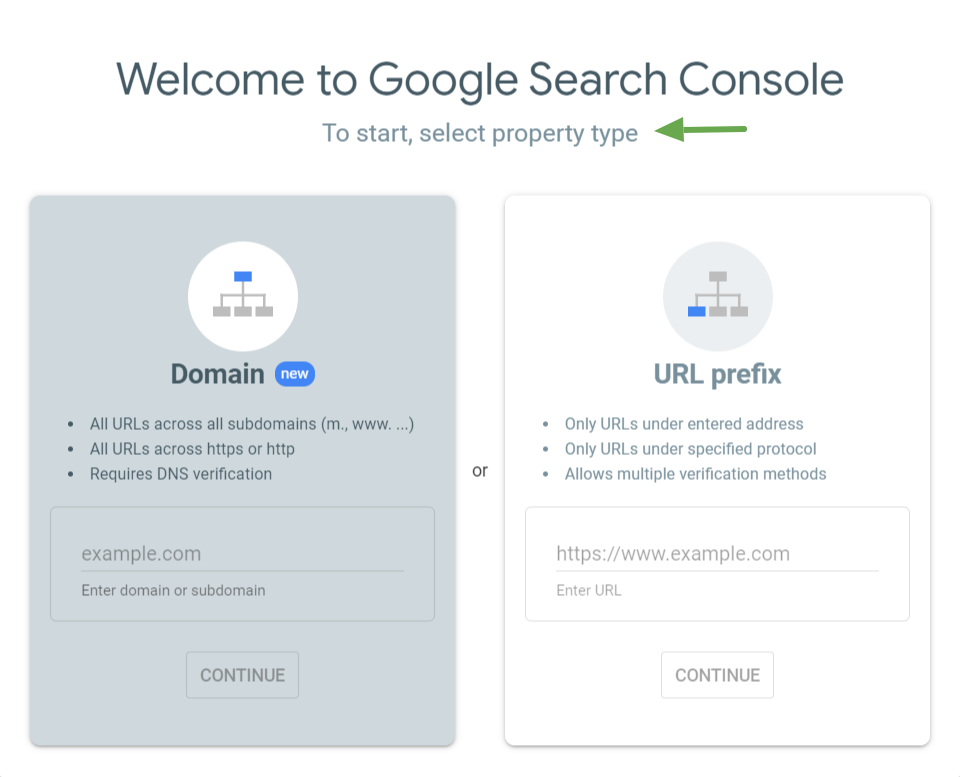
If you don’t already have one, go to Google Search Console’s official page to create an account.
Next, select a property type by adding your website address to either the domain or URL prefix tab (as seen below).
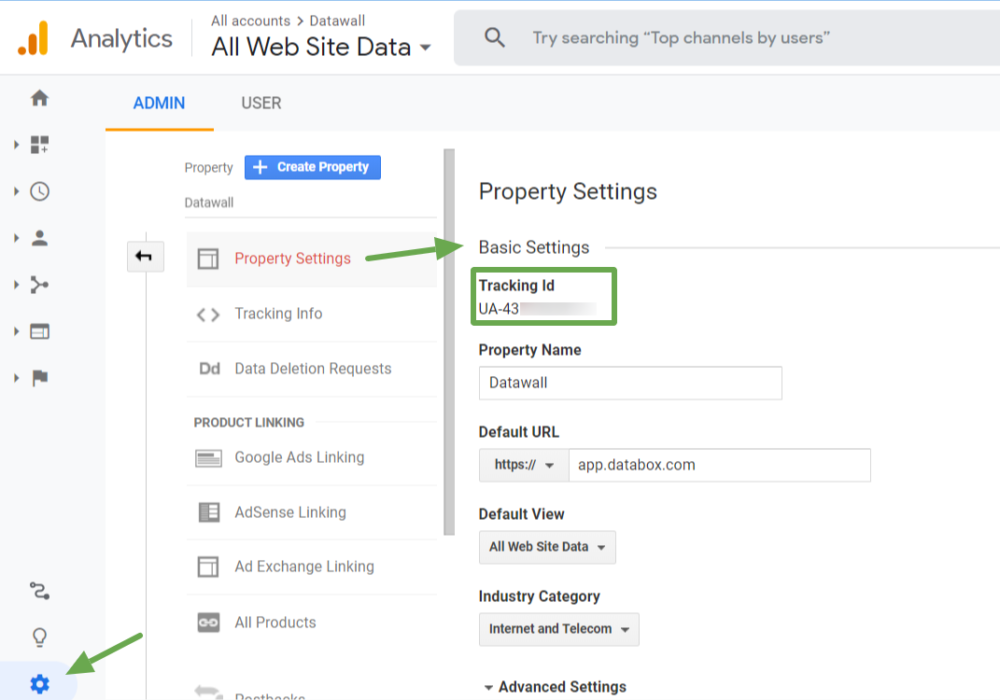
Lastly, verify that you own the site by using your Google Analytics tracking ID.
Quick reminder: The Google Analytics tracking ID can be found in Admin > Property Settings > Basic Settings > Tracking ID.
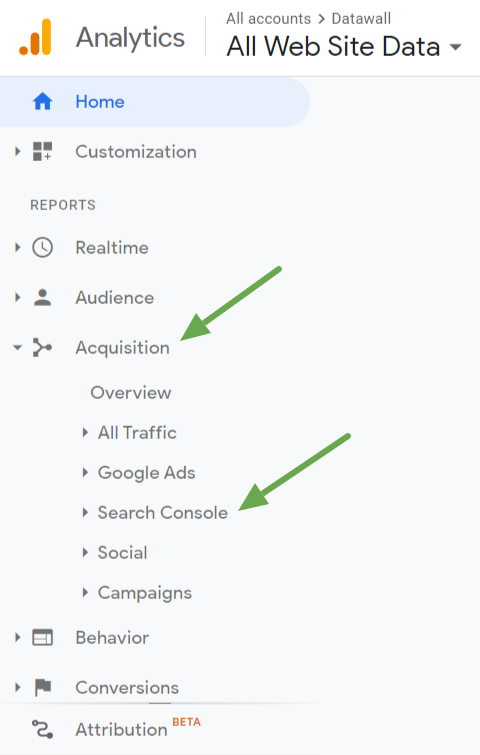
The next time you log in to your Google Analytics account, you’ll be able to access Google Search Console via the sidebar as well.
Verify Site Ownership
To access data from Google Search Console, as we mentioned, you need to verify site ownership. Other than using your Google Analytics tracking ID, there are two ways you can do this depending on the property type you added.
The first one is Domain Property Verification, and you can start by checking if your domain is registered with any of the listed providers.
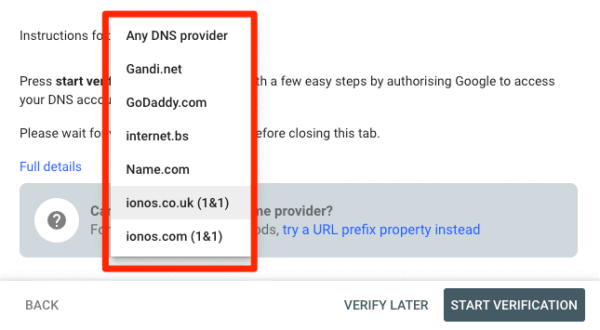
If so, select your provider and hit the “Start verification” button. From there, you just need to sign in to your account and follow the instructions.
If you can’t find your registrar, select “Any DNS provider.”
Then, proceed to sign in to your account with your domain provider, select your domain, and look for an option to manage DNS or Domain Name Servers.

Choose the option to add a TXT record, and then paste in the record from Google Search Console. Save it and verify it.
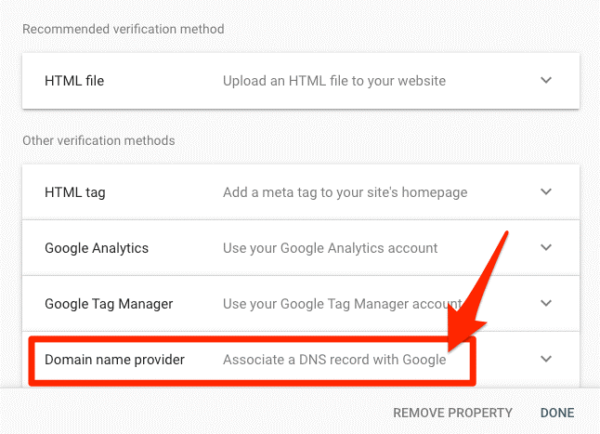
The second verification type is URL Prefix Property Verification.
There are several ways you can do this, but the recommended method is to upload an HTML file to your website.
Add a Sitemap to Google Search Console
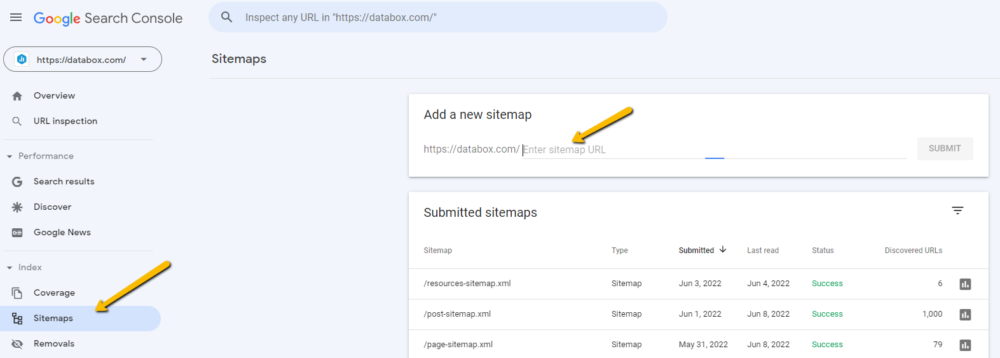
Adding a sitemap to Google Search Console is important because it helps Google find and crawl important content on your website.
To submit a sitemap to Search Console, go to “Sitemaps”, and simply paste the URL of your XML sitemap into the box labeled “Enter sitemap URL”. After that, hit “Submit.”
Add a User to Google Search Console
Users are people who have access to some or all of the data in Google Search Console.
A user can be an Owner, Full User, or Restricted User.
When you verify a property in the Search Console, you become an Owner.
This means you can add new users by navigating to Search Console > Choose a property > Settings > Users and permissions > Add user
Type their email address and select either full or restricted access. To revoke or changes access, you can always come back and adjust your settings.
Understanding Google Search Console Features and Reports
Google Search Console provides a handful of different reports and features that SEOs can use, but navigating through them isn’t exactly simple.
Let’s go through an overview of the different Google Search Console SEO reports and features and explain what they’re all about.
- Google Search Console Overview
- URL Inspection Tool
- Performance Report
- Index Report
- Experience Report
- Security Issues Report
- Manual Actions
- Links Report
Google Search Console Overview Report
When you open up your Google Search Console account, the first thing you’ll see is an Overview report, which includes a brief summary of your website/property.
It’s essentially an overview of your website’s most significant data within GSC.
The Overview report captures metrics like manual actions, indexed pages, and more. Plus, you can see more specific things like Search Analytics, Sitemaps, and Crawl Errors by opening one of the listed links.
You can use this report to identify larger issues quickly and check out how your site’s performing overall.
URL Inspection Tool
The URL inspection tool lets you see how Google views a specific page on your website.
You can use the tool to check whether a page is crawled or indexed by Google and troubleshoot the issue in case the page doesn’t appear in search results.
Additionally, you can identify errors linked to mobile usability, HTML, and JavaScript and let your development team know that they should be fixed.
To use the tool, simply copy-paste the URL of the desired page and click enter.
This will prompt a window where you’ll be able to check out page results and see whether the URL is indexed.
Performance Report
The Performance Report offers users valuable insights into your website’s search performance.
The first part of this report showcases search features such as featured snippets.
You can explore four different search types, including Web, Image, Video, and News.
The Web search is set by default, but you can change it by pressing the ‘Search Type’ button.
At the top of the Performance Report, you will see four metrics displayed:
- Total Clicks – How often users click on your website in the search results.
- Total Impressions – The number of times your website appeared in a search result.
- Average CTR – Percentage of the average number of times users click on your website in the search results.
- Average Position – As the name suggests, your website’s average position in search results.
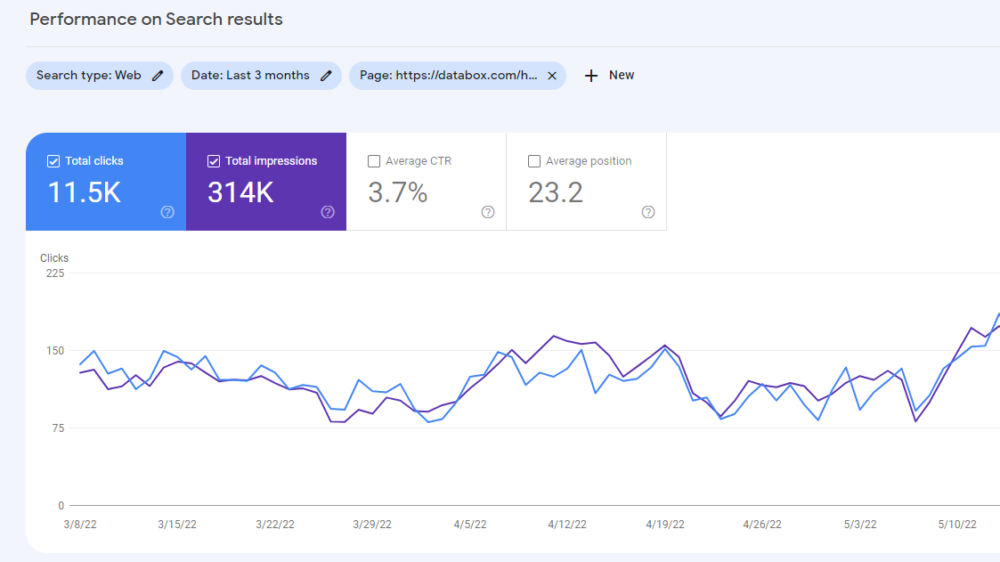
At the bottom part of the Performance Report, users can find six different dimensions of performance data:
- Queries – Displays the highest search queries and keyword performance.
- Pages – Displays the best-ranked web pages.
- Countries – Leading countries
- Devices – Shows which devices visitors most frequently use (mobile, tablet, and desktop).
- Search Appearance – Shows which types of results the website was displayed in.
- Dates – Sorts the impressions and clicks by date.
Index Report
The index report shows you whether Google is crawling your website and if there are any problems preventing your pages from getting indexed.
Once you open up the report, you’ll notice a simple chart that displays changes related to the number of indexed pages (in the last 90 days).
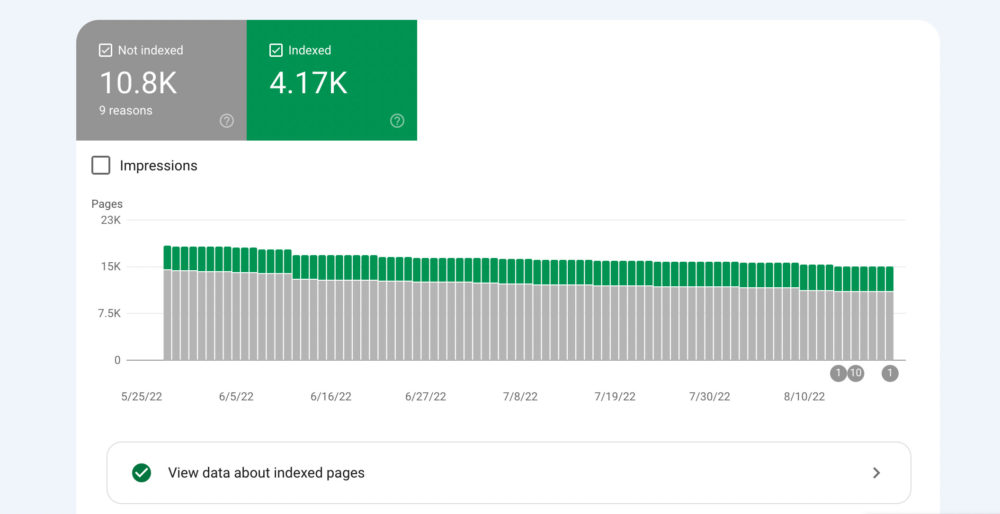
There are four colors that represent different statuses:
- Red – Error
- Yellow – Valid with warning
- Green – Completely valid
- Grey – Excluded
Naturally, you’ll want to deal with the errors first since they present the biggest issue when it comes to your content getting indexed.
Experience Report
The Experience report provides you with data related to your website’s visitor’s user experience.
In this report, Google examines experience metrics for specific URLs on your website and uses them as ranking signals for search result URLs.
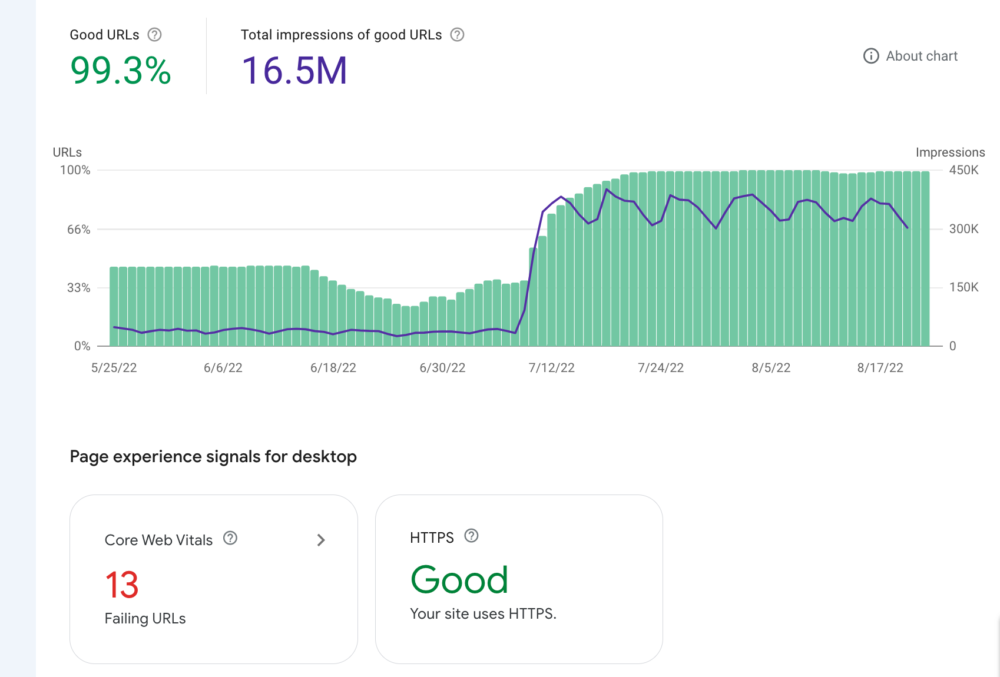
This is the criteria that Google uses:
- Core Web Vitals – Tests your website’s page loading speed, responsiveness, and overall stability. You can get a rating of Good, Needs Improvement, or Poor.
- Mobile Usability – To rank for a ‘Good’ status on mobile devices, there mustn’t be any mobile usability errors in the mobile URL.
- HTTPS Usage – Pages have to be served over HTTPS to get a ‘Good’ page ranking in Google search.
Security Issues Report
The Security Issues report showcases any information that might suggest your website has been hacked or if it’s acting suspiciously and could potentially harm a visitor.
By ‘acting suspiciously,’ Google refers to phishing attacks and installing malware on the visitor’s computer.
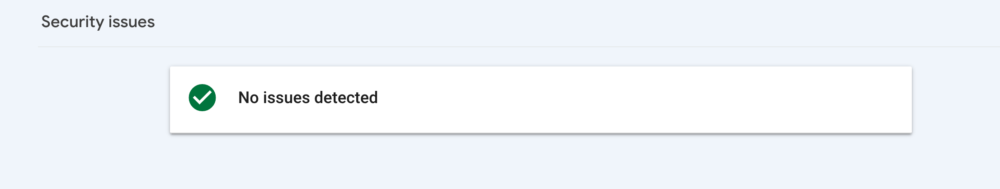
If your page is hit with a security issue, there will typically be a warning label in the search results or a warning page when visitors try to open the page.
There are three categories of security issues:
- Hacked content – Content on your website that was posted without your permission.
- Malware/Unwanted Software – Software created to harm a visitor’s device.
- Social Engineering – Dangerous content that can make the visitors do something risky (e.g. reveal personal information).
Manual Actions
This report shows you whether there are any manual actions issued against your website.
In other words, whether there are any pages that aren’t compliant with Google’s webmaster quality guidelines, which results in search result shadow bans.
If one of your pages is affected by manual action, you will receive a notification in the Search Console message center.
Links Report
The Links report displays all the links pointing to your website.
However, you should know that this report doesn’t showcase links that influence your site’s search result ranking.
Instead, it only focuses on links that aren’t helping with the SERP rank.
There are columns in the report – external and internal links.
For external links, there are three reports, including Top Linked Pages, Top Linking Sites, and Top Linking Text.
For internal links, there is only one report – Top Linked Pages.
Each of these reports includes a gateway to additional results that can be clicked to view.
For instance, if we expand the Top Linked Pages report, we’ll be able to see Top Target Pages (most frequently linked pages from the website).
PRO TIP: How to Improve Your Google Rankings
To optimize your website for organic search, you probably use Google Search Console to learn which pages receive the most impressions and clicks, and which queries drive them. To get the information you need, you may need to visit several areas within GSC and view multiple reports.
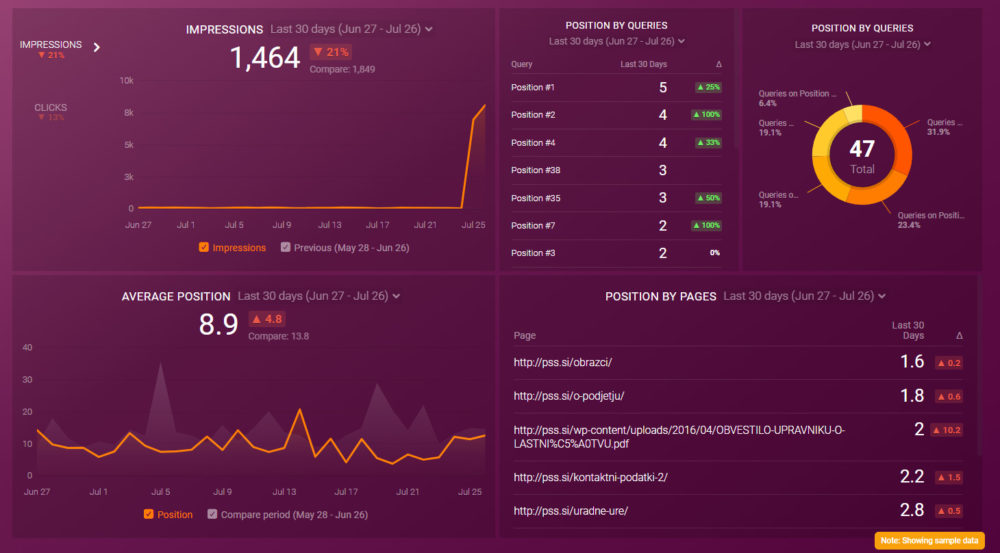
Now you can quickly assess your overall SEO performance in a single dashboard that monitors fundamental metrics, such as:
- Impressions. See how many impressions and clicks your website pages receive in Google.
- Average position. Track your average search position and monitor daily, weekly, or monthly fluctuations.
- Position by pages. Learn the search results page position of any page on your website.
- Position by queries. See how many search queries each position group receives.
And more…
Now you can benefit from the experience of our Google Search Console experts, who have put together a plug-and-play Databox template showing the most important metrics for monitoring your SEO performance. It’s simple to implement and start using as a standalone dashboard or in marketing reports!
You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your Google Search Console account with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
How to Use Google Search Console for SEO: 20 Pro Tips
Now that we’ve covered some of the basics regarding Google Search Console, let’s check out the tips that the SEOs we surveyed recommend.
We talked to 100+ marketers, and here are some of the best Google Search Console SEO tips that they shared.
- Use Search Console for Keyword Research
- Check Your Average Position for Specific Queries
- Check for Website Coverage Issues
- Identify Crawl Errors and Unindexable Pages
- Optimize Your Website Pages for Mobile Search
- Check Your Backlink Profile
- See if Your Site Has Any Penalties
- Use International Targeting Report for Prioritizing a Specific Country in Search Results
- Analyze Mobile vs. Desktop Traffic
- Prevent Keyword Cannibalization Issues
- Check the Canonical Domain Settings
- Change Meta Tags and Monitor the CTR Impact
- Monitor high CTR Keywords and Optimize Around Them
- Find Exploding Topics
- Find Internal Linking Opportunities
- Compare Your Search Performance to Previous Periods
- Determine Which Pages Are Wasting Your Crawl Budget
- Decrease Your Bounce Rate by Identifying Negative Keywords
- Give Google More Information about Your Site without Adding Structured Data
- Find FAQs in Google Search Console with RegEx
Use Search Console for Keyword Research
Google Search Console’s Performance Report contains many of the basic pieces of data you’ll need to rely on for SEO. One of those is the keywords that your site and pages rank for, called “queries” within the tool.
To use Google Search Console for keyword research, get started by logging in to the tool, clicking Performance, and scrolling down the page to reach the Queries tab.
The Queries tab will be selected by default.
Below it, you can scroll and page through the list to see every keyword you show up for in search results across your entire website.

If you want to see what keywords your individual pages rank for, you’ll need to take a couple more steps. First, click the Pages tab, and then select the page you want to review.
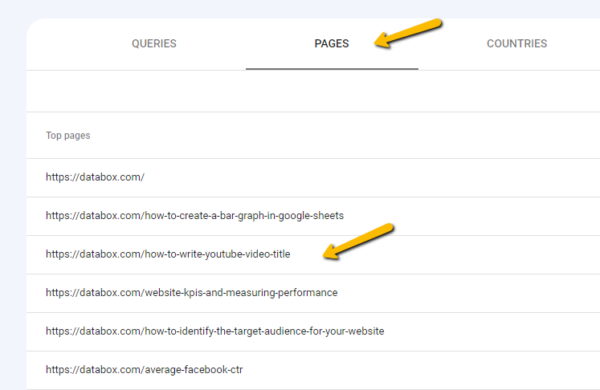
Now, click the “Queries” tab again. Here, you’ll see all of the keywords that the specific page you selected in the last step ranks for.
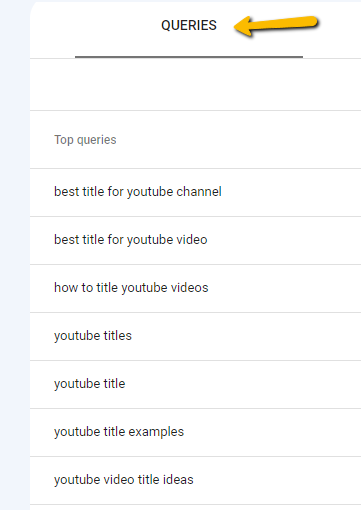
If you want to look at keywords for a different page, return to the Pages tab, dismiss the currently selected page, select the next page you want to view, and click Queries again.
Additionally, Google Search Console’s keyword tool can also be used for improving local SEO.
Here’s how Tony Mastri of MARION Marketing Agency does it.
“I habitually add a URL query to the primary website field within GMB, then use Google Search Console to see what keywords searchers are using to find and click on my local results,” says Mastri.
“By using the Exact URL page filter in GSC, you can differentiate standard organic clicks to a page vs. local organic clicks to a page. This provides granular search term information that can be used to advance local SEO efforts.”
Related: 14 Free Ways to Research and Analyze Keywords for Blog Posts
Check Your Average Position for Specific Queries
Another metric available in the performance report is the average position. Position refers to where you’re ranked in the search results for specific keywords.
If you’re in the top results, your position is 1. If you’re at the top of page two, your position might be 11.
Average position is an average (sum of positions divided by the total number of keywords) of your positions for every keyword you rank for.
Even though average position isn’t the best indicator of your site’s overall health, a good average position in GSC is considered anything around 30 or lower.
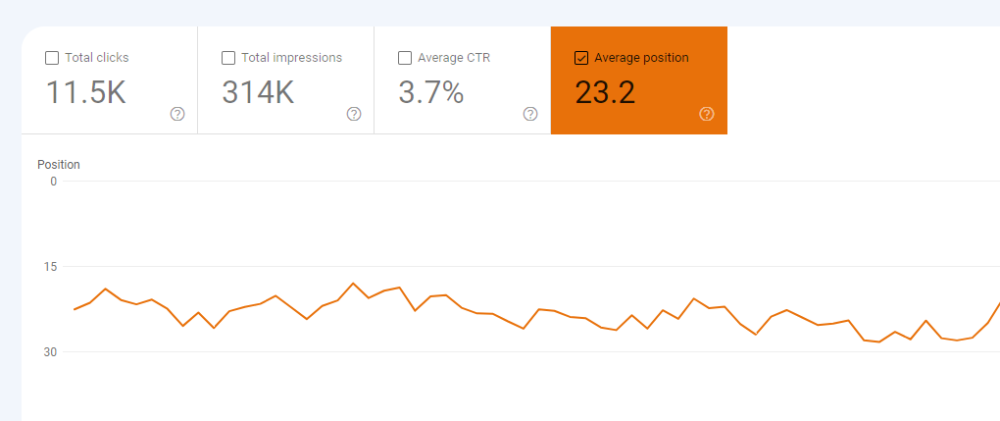
The general report shows the average of your positions for every keyword your entire site ranks for. If you filter by page, it shows the average of positions for all keywords a specific page ranks for.
For this reason, the average position usually isn’t the most helpful piece of data. However, if you scroll down to the table below the graph, it will show you what position you rank in for each individual keyword. And this data can be much more insightful.
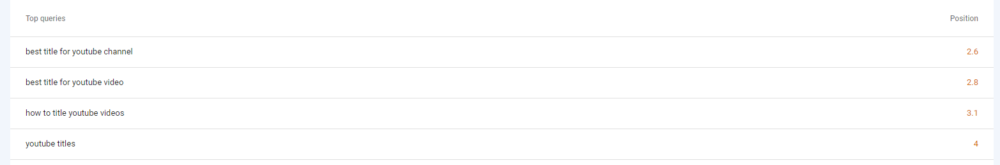
Using this data, you can not only see exactly where each page of your site ranks for specific keywords, but also use it to monitor how your rankings change after you make on-site adjustments and optimizations.
Related: 29 Ways to Improve Your Search Position in Google Search Results
Check for Website Coverage Issues
Using Google Search Console’s Coverage Report, you can see exactly how many pages of your site Google has indexed.
Click Pages within the index report to see the data.
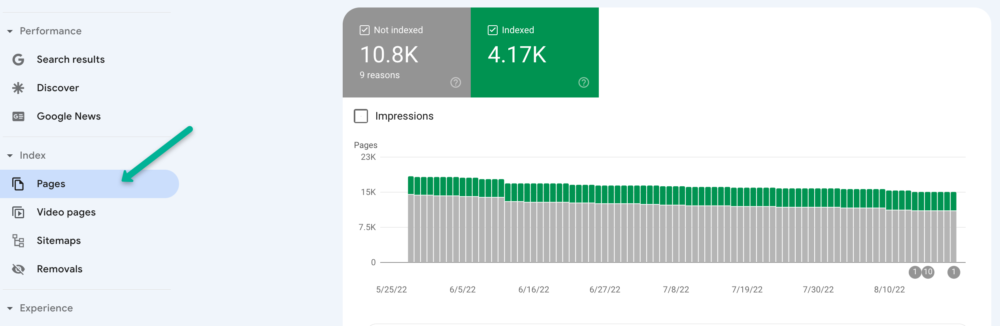
For larger sites, it’s recommended to compare the number of pages that you’ve submitted via XML sitemap with the actual number of pages that have been indexed by Google.
This is one of the most important steps to take in order to determine if your site has crawling, indexing, and/or content duplication issues.
If you find that a specific page of your site isn’t in Google’s index, you can submit it for indexing using the URL inspection tool:
- Click URL inspection.
- Paste the URL you want to submit into the search bar and wait for Google’s test to complete.
- If Google doesn’t find any errors, click Request Indexing.
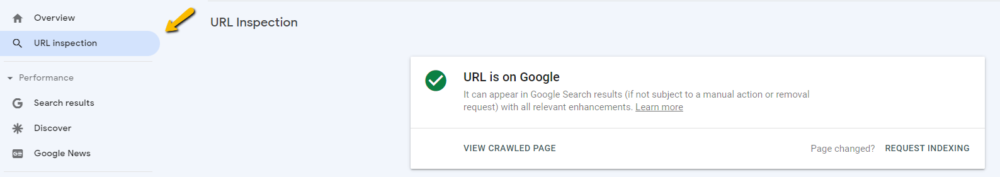
It may take anywhere from a few hours to a few days for Google to process your request, crawl the page, and add it to its index.
Identify Crawl Errors and Unindexable Pages
Sometimes, developers will add canonical or no-index tags to a page to temporarily prevent Google from crawling it, but they may forget to later remove those tags.
Other times, you delete a page and forget to redirect it to a new page.
Fortunately, Google Search Console logs issues for these types of problems, so you don’t need to inspect the HTML of each page to look for errors.
You can find these errors in the Index report by clicking Pages and reviewing the data presented. Google Search Console will tell you why certain pages haven’t been indexed.
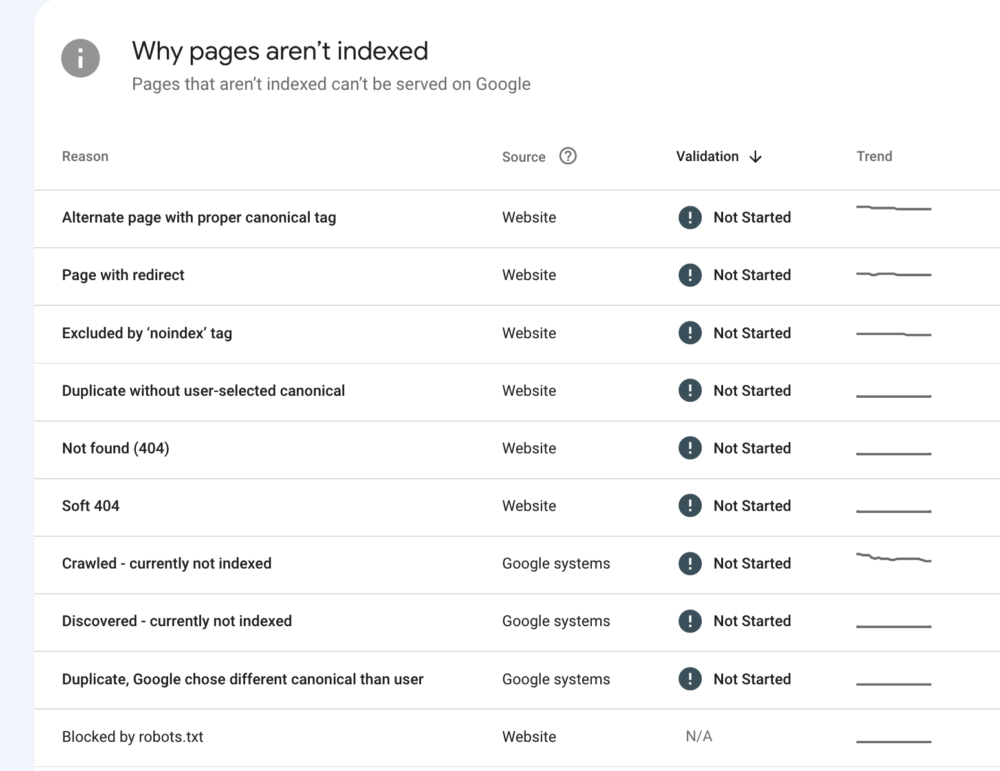
Google Search Console Page indexing tool not only shows which pages aren’t indexed, but it also explains why those pages weren’t indexed. It can help you identify a range of issues, such as developer mistakes in indexing, 404 errors on pages, and more.
404 errors are usually a result of old or broken links which have previously been indexed by Google. But with this feature, you can easily find URLs on your domain that are producing them.
Related: Google Analytics 404 Report: How to Monitor, Find and Fix 404 Errors in GA
Optimize Your Website Pages for Mobile Search
With Google rolling out its mobile-first indexing, it’s now more crucial than ever that all pages on your website are mobile-friendly.
Luckily, Google Search Console makes it easy to find any mobile page issues.
Just click on “Mobile Usability” and look to see if you have any errors. If so, scroll down the page to get more details.
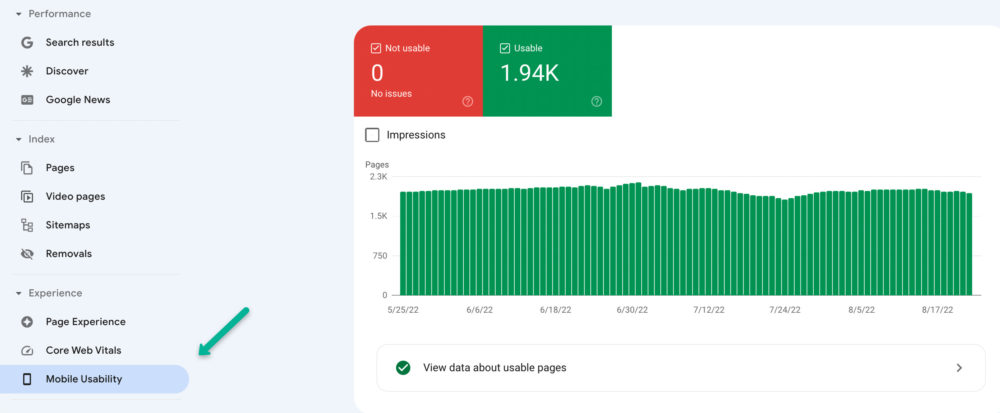
Google Search Console allows you to quickly check if the pages on your website are responsive and whether they load quickly, as well as if all the elements on the page fit well (such as ensuring fonts aren’t too small to read on mobile).
The best thing is that this tool will also tell you what needs to be corrected. This ensures that your webpages are providing a better mobile experience for visitors—and that they end up ranking higher in search.
Check Your Backlink Profile
Google Search Console’s Links Report shows you what sites have linked to your site, what pages other sites link to most often, and what pages have the most links.
To see all of your site’s backlinks, click the “Links” tab, then click “More” under “Top linking sites” to view all of your inbound links.
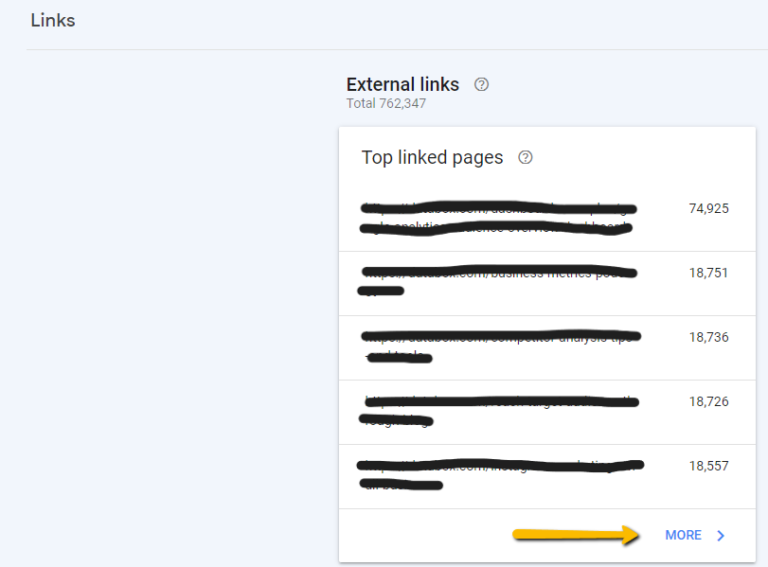
Related: 30 Free Link Building Tips for Building Links On Little-to-No Budget
See if Your Site Has Any Penalties
If Google determines that your site violates its quality guidelines, it can issue a manual action against your site, which could result in your entire site getting removed from its index.
Typically, manual actions are the result of things like buying backlinks, publishing scraped or low-quality content, keyword stuffing, or sneaky redirects.
If you or someone you’ve hired to work on your site ever engaged in any questionable practices to boost your SEO, it’s worth checking to see if you’ve been issued a manual penalty.
But, you can also be issued a manual penalty for things other people did to your site.
If Google believes your site was hacked, it may remove it from its index. It can also issue a penalty if your site is full of low-quality comments with links that point to questionable sites.
Hopefully, manual penalties aren’t something you’ll ever have to worry about, but if your traffic drops rapidly and you aren’t sure why, it’s worth checking the “Manual actions” report to see if you’ve been issued a penalty. If so, you can find instructions for how to fix the issue and get your site reindexed.
Use International Targeting Report for Prioritizing a Specific Country in Search Results
The International Targeting report includes a “Country” tab that site owners can use for prioritizing specific countries in search results.
This is important because search results can be different for a user in Greece and a user in the UK.
If you use a generic domain (.com or .org) you can help Google pinpoint which countries matter the most to you.
On the other hand, if your use a country-coded domain (e.g., .fr), you are already associated with a geographic location (in this case, France). This disallows you from specifying a geographic location.
“One tip for using Google Search Console to track SERPs would be to keep an eye on the countries tab that shows your results,” says Anjana Wickramaratne of Active Digi Solutions.
“Some people only care about the Google Search Console queries that they rank for, but in reality, the countries that they rank for are valuable as well. By monitoring the countries in your SERPs, you are able to adjust your future SEO strategies to target the countries that you want.”
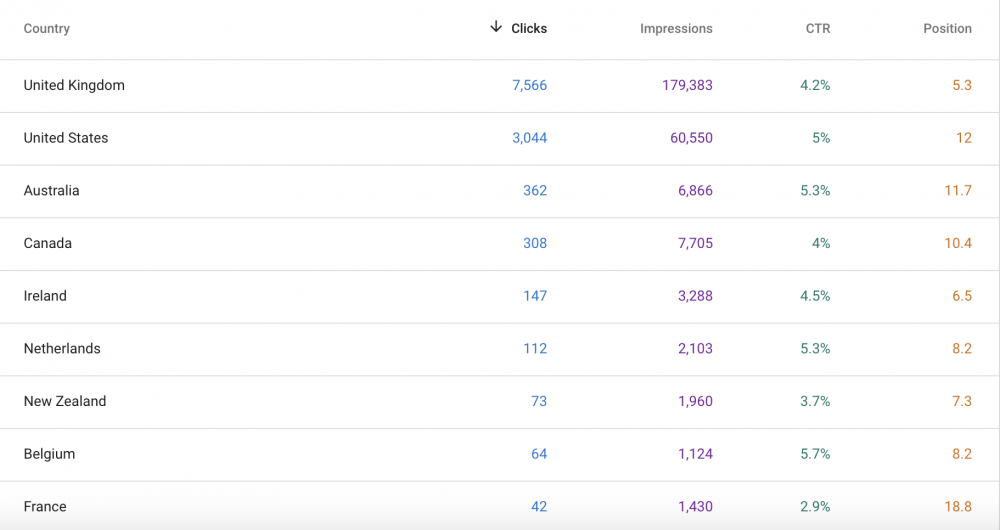
Analyze Mobile vs. Desktop Traffic
To stay on top of both “fronts,” you should make an effort to analyze both mobile and desktop traffic and figure out ways to optimize them.
A lot of companies make the mistake of focusing solely on desktop traffic, despite the fact that more searches are conducted on mobile devices (64%) than on desktop (36%).
Finn Hayden of You Well recommends: “look at devices within the performance report. Most businesses forget that the majority of their traffic is likely to be coming from mobile devices and that their mobile rankings will likely differ from their desktop rankings.”
“Within the performance report in Search Console, there is a Devices section where you can see which devices are driving the most traffic to your site.”
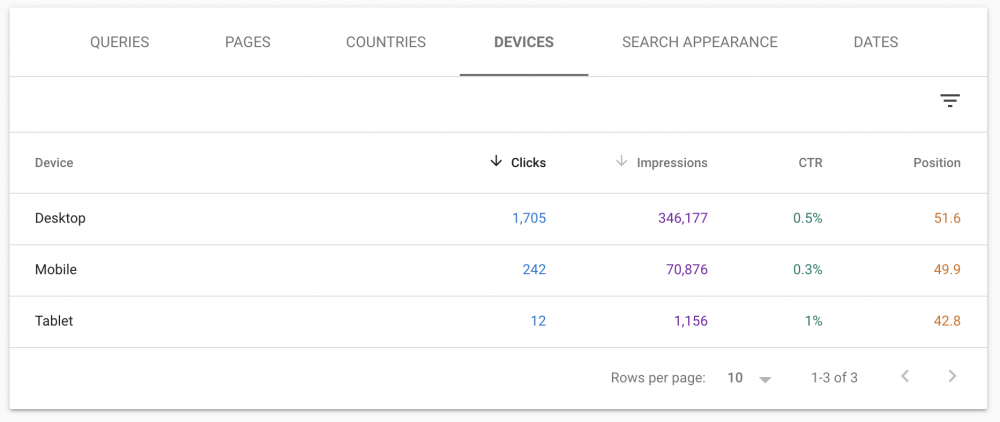
Hayden explains: “You can pull out some great reports from here that will really help show you if your SEO work is effective. For example, you should see a gradual increase in mobile traffic if your SEO is working.”
Related: A Beginner’s Guide to Mobile Website Optimization
Prevent Keyword Cannibalization Issues
Keyword cannibalization is when the content on your site includes too many identical/similar keywords and leaves Google confused on which page to rank higher.
This can be a problem when a web page that you didn’t want to prioritize gets a higher ranking.
Here’s what Candour‘s Kiera Lavington says about this issue, “identify potential keyword cannibalization issues using the Performance Report by filtering to a target term with the Query filter. View the pages which rank for the selected term and then filter to compare the top 2 pages (by impressions) using “Compare” in the pages filter.”
“By using the “Impressions” or “Average Position” tab, you can see where pages dropped in and out of Google’s search results for the target term.”
“This will not be conclusive in identifying a cannibalization issue but will set you on your way if you can spot instances where one of the pages starting to rank causes the other page to drop,” Lavington continues.
“With further exploration, you can determine whether this is a cannibalization issue or not.”
Check the Canonical Domain Settings
The canonical domain is the domain version that stands as your preferred indexing version.
Google uses this information to penalize duplicate content and let the search engine know which domain you want indexed.
Voro’s Tomas Hoyos says you should “make sure to select the canonical domain you prefer within Google Search Console.”
“In other words, you should specify whether you prefer “”www”” in front of your domain name (e.g., www.voro.com), or not (e.g., voro.com).”
“f you don’t do this, Google might view the www and non-www versions of your domain as distinct, which means that you will divide credit for clicks, page views, backlinks, and engagement between two domains. This will hurt your SEO,” Hoyos explains.
Change Meta Tags and Monitor the CTR Impact
Meta tags are the text snippets that pop up below the article name and describe the content in that article.
They only appear in the page’s source code, not the page itself, and are mainly used for telling Google what the web page is all about.
These text snippets have a lot of influence on off-page SEO, which is why it’s recommended that you test different meta tags and see how they impact your overall CTR.
“We always pay close attention to the CTR of our top keywords and pages,” says Sanitycheck‘s Nick Swan. “From our internal data, we have seen that when we consistently drive up our CTR, our rankings improve over time.”
“We update title tag and Meta descriptions each month and run tests to see if our new copy can improve our CTR. Just like we would test ad copy in Google Ads, it is critical to be running organic search snippet tests as well.”
Related: 18 Ways to Write a Perfect Meta Description to Boost Your CTR
Monitor High CTR Keywords and Optimize Content Around Them
By monitoring which keywords have a high CTR rate, you can pinpoint specific keywords worth optimizing for.
For instance, if you’re focusing on 2 different keywords on your website and one has a better CTR rate, it can become more favorable for your site even if it has a lower search volume compared to the other one.
That’s why Lynn Hericks of Intuitive Digital recommends “optimizing and expanding old blogs on your site by using keywords that are already working!”
“In the Performance section of Google Search Console, filter your queries by page to see what terms a blog already ranks for—find relevant keywords that rank on average in positions 8-20 (a term that you weren’t necessarily targeting directly, but your content still shows up for).”
“Now go back to edit your blog post and specifically use those terms to expand content for a rankings boost!” Hericks explains.
Pyxis Growth Partners’ Parker Short recommends using Google Analytics to find the pages that drive the most traffic to your site, then using Google Search Console to find the data you need to optimize those pages even further.
“Look to see what terms each page ranks for that are in positions #2-10 in search results and focus on those. Take those terms (if they’re relevant) and try to work them in naturally into the copy on that page.”
“This is a great way to optimize historical blog posts that may pull in some organic traffic but are underperforming given the high quality of the content,” Short says.
Related: Blog SEO: 47 Expert Tips for Optimizing Blog Posts for SEO
Find Exploding Topics
Google Search Console can be used to spot upcoming trends. If you created a new category of product, or simply wrote a new article, use the Search Results performance report and filter your content to the most recent dates to see where new organic search traffic is landing.
You can also look at impressions, CTR, and average ranking to predict where traffic will soon be seen.
This information will allow you to audit that page’s keyword targeting, review the copy, improve internal navigation, and more.
TJ Kelly explains how they do this at RaySecur, Inc:
- “Open your Performance Report
- Navigate to the Pages tab
- Sort by Impressions (high to low), to see which pages appear in SERPs the most
- Click on one of your important/valuable pages
- When the report refreshes, click the Queries tab
- Edit the date scope and select Compare, then “Compare last 3 months to previous period”
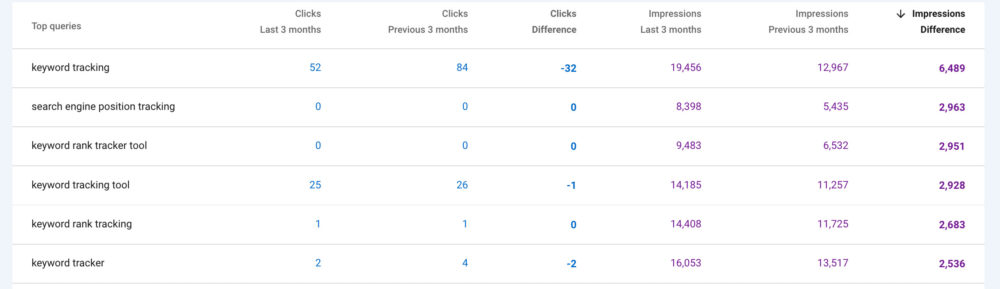
Kelly explains: “You can now sort by Impressions, for both Last 3 Months and Previous 3 Months, to see which queries are driving more (or less) SERP impressions for a given page.”
“The key is to find Queries that appear high on the Impressions list for Last 3 Months, but did NOT generate as many impressions on Previous 3 Months—that may indicate the page ranking for new Queries, or that these new Queries are gaining search volume, and would therefore represent new traffic opportunities.”
“Bonus points if you export the report to a spreadsheet and calculate the change, then sort by change value. This shows the biggest movers (up or down) over time,” Kelly continues.
“Combine this insight with your Click numbers to see if the increased Impressions are translating to more clicks/traffic—an indication that your ranking is improving or maintaining—or, if Impressions went up, but Clicks did not, your positions may be falling.”
Related: 20 Ways to Fill Your Editorial Calendar with Highly Relevant Topics
Find Internal Linking Opportunities
Aside from checking the status of your links, you can also use Google Search Console to find suitable internal linking opportunities.
“The one tip I recommend is to use GSC to find pages that need internal linking,” says WPBeginner‘s Faizan Ali. “To find pages that need internal linking, click more under the top linked pages and then click on the internal links.”
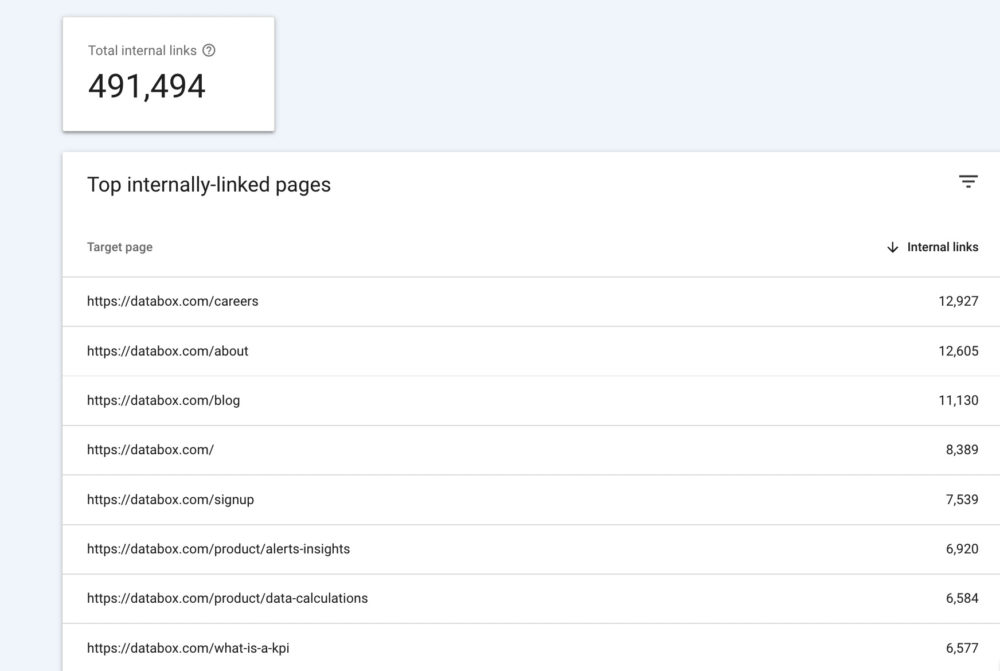
Ali continues: “There are two main advantages of internal linking:
- They may help your new page get indexed faster.
- They will transfer PageRank to the new page, which may help it rank higher in the search results.”
“In order to find internal linking opportunities try this search operator “site:yourdomain.com ‘keyword you want to internal link,” Ali explains.
Based on the opportunities found, make sure you create repeatable internal linking strategies to ensure continual growth.
Compare Your Search Performance to Previous Periods
Web performance over a specific time period is one of the most important yet overlooked features in Google Search Console.
It can provide you with valuable insights into whether your SEO efforts are paying off or if you need a change of strategy.
Digital Debut‘s Deniz Doganay shares: “I really like to use the performance section to compare yearly quarter vs. quarter.
There are quite a few insights you can gather from this. Some being, checking rankings positions currently vs before, as well as clicks and impressions. It also gives you a good idea of your click-through rate.”
“Sure, you might have much better rankings now, and higher impressions but may notice that your CTR is a lot lower,” Doganay continues. “You then may need to work on your CTA’s or your meta title/descriptions or may even look into what you are doing on other channels to capitalize on these missed opportunities.”
PRO TIP: Looking for ways to track your organic search and learn which keywords and landing pages are ranking best? Learn how to use Google Search Console, Accuranker, and Databox to determine which topics and keywords you should focus on to improve your content marketing strategy.
Determine Which Pages Are Wasting Your Crawl Budget
Google doesn’t necessarily always crawl every page of your website. It sometimes establishes a crawl budget, limiting the number of pages of your site that it crawls regularly.
This can be an issue because it could lead to new/updated content getting ignored by Google’s crawlers (i.e. your new/updated content won’t appear in search results).
For small sites, the crawl budget usually isn’t an issue. But if you have a site with thousands of pages of content, it can be. According to Google, “having many low-value-add URLs can negatively affect a site’s crawling and indexing.”
Indigoextra’s Martin Woods says that Google Search Console can help you find low-value pages that may negatively impact your crawl budget: “Google Search Console is very useful for finding the pages on your site that nobody visits anymore.”
To do this, look for pages that get the least number of impressions and clicks. Then, either delete them, 301 redirect them to pages that contain similar content, or update the content on the page to make it better.
“Studies have shown that if you delete pages with very little or no traffic—or 301 redirect them to better pages—Google will value the more relevant pages more. Overall, this substantially increases the traffic to your site as a whole,” Woods says.
Decrease Your Bounce Rate by Identifying Negative Keywords
“One advantage of using Google Search Console to see what keywords your site is ranking for is to identify negative keywords,” says Sam Makwana of Traffic Radius.
Negative keywords are queries that you’re ranking for but really shouldn’t be because your content doesn’t satisfy the user intent behind that keyword. According to Makwana, this can have a negative impact on your bounce rate. “With appropriate corrective measures, you will be able to decrease your bounce rate.”
One way to do this is to update the content to more appropriately address keywords you’re ranking for but haven’t really covered in your content.
Another approach may be to create a new piece of content that does address the intent of a negative keyword, then link to that new post from the existing post that’s already ranking for the negative keyword.
Give Google More Information About Your Site without Adding Structured Data
Adding structured data to your site gives Google more information about your content. For example, you can use structured data to specify whether a piece of content is a general article, a list of FAQs, a recipe, a job posting, a review, and more.
Structured data helps Google understand your content better and can result in expanded search result listings. For example, here’s a search result that contains structured data for both a recipe and ratings; both of these pieces of data lead to a more detailed search result:
But as Primitive Social’s John Hodge says: “Not all SEOs are experienced with web development, and sometimes even code-confident SEOs simply don’t have access to website code.”
“With the data highlighter in Google Search Console, you can customize a site’s appearance on search result pages. This makes pages stand out, improves rankings, and gives more context to Google about your content.”
“Using the data highlighter makes it easy to tag different pieces of content on a website without adding structured data to your site code. Also, it’s super easy. All you do is select the item you’ll be highlighting (software, reviews, restaurants, etc.), enter the URL of the page, and start highlighting.”
“When you highlight a piece of content, you can then specify more information about it, like if it’s a picture, an official URL, a download URL, and more.”
“Google ranks items based on contextual cues, and using the data highlighter is an efficient way to improve the context of your website content.
Related: The Best Structured Data Tools for SEOs and Content Marketers
Find FAQs in Google Search Console with RegEx
In 2021, Google Search Console started supporting RegEx in filters.
This was received positively by Google Search Console users, as this new feature unleashes many opportunities to gather valuable data.
RegEx stands for “Regular Expression” and it’s basically a sequence of characters that forms a search pattern that can be used to check if a string contains a specified search pattern.
There are a lot of use cases for RegEx in Google Search Console, but one of the most useful is finding keywords that are related to different user search intent.
The eCommerce SEO expert Luca Mussari explains how:
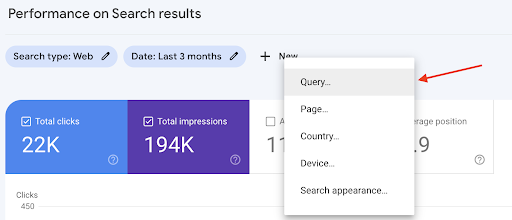
- Go to the “Performance” report
- Add a filter by clicking on “New” next to “Date: the last 3 months”
- Choose “Query”
4. In the dropdown you see, select “Custom (regex)”
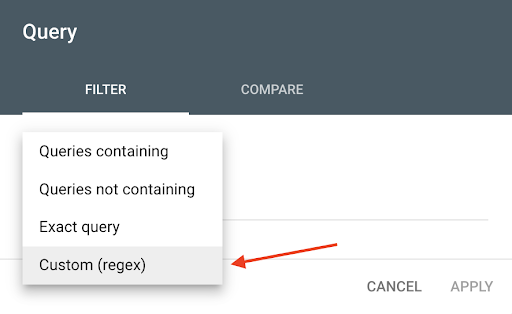
5. Then select “Matches Regex” to find all the search queries containing one or more words from the RegEx formula.
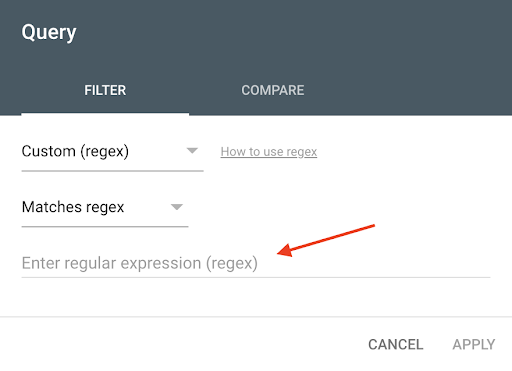
6. Add the following RegEx based on the search intent you want to gather data from:
Navigational
.*yourbrandname.*
Informational
who|what|where|when|why|how|was|did|do|is|are|aren’t|won’t|does|if|can|could|should|would|won’t|were|weren’t|shouldn’t|couldn’t|cannot|can’t|didn’t|did not|does|doesn’t|does not|would not|wouldn’t|
Commercial
.*(best|compare|top|vs|review*).*
Transactional
.*(buy|cheap|affordable|price|purchase|order).*
Related: Useful Regex Codes for Google Analytics Reporting
Automate SEO Reporting with Databox
Determining indexed pages, finding quality links that improve your rankings, identifying the most popular keywords… Google Search Console is one hell of a free SEO tool to have at your disposal.
However, we won’t sugarcoat the fact it’s also probably one of the most difficult tools to learn the ropes of.
Even with so many valuable insights to extract, finding them and categorizing them can feel like going through a maze, not knowing which turn to make.
Not to mention that all the data is scattered across various tabs and queries, adding to the confusion even more.
But does that mean that you should give up on insights that could potentially skyrocket your SEO?
Absolutely not!
Instead, you should use dashboard software that makes understanding Google Search Console data and putting it to work a whole lot easier – enter Databox.
With Databox, you can connect your GSC account, drag and drop your most important metrics, and visualize them with a few clicks on a button – all in one dashboard.
You’ll be able to track all the crucial metrics like impressions, clicks, CTR, average position, and more in one place.
The process of building a dashboard literally takes minutes.
But, if even that doesn’t fit your schedule, you can always use our dashboard setup by contacting someone on our team and letting them know what you want out of your custom dashboard.
We’ll have it delivered as soon as in the next 24 hours.
Sign up for a free trial now and streamline your SEO reporting process with Databox.