Table of contents
Imagine having a crystal ball in your company and a fortune-telling department that would operate the ball.
You would be able to not only predict future events and their impact on your business, but you would also be ready to face them by creating recovery strategies and continuance plans.
Unfortunately, crystal balls are a bit hard to find these days, but we do have something pretty similar – business impact analysis reports.
You can look at a business impact analysis report as your crystal ball and the BIA practitioners as the fortune-telling department.
Business impact analysis is used to anticipate the consequences that disruptive events could have on your business operations and activities if they were to happen.
In this guide, we are going to teach you what BIA reports are, why they are important, how to conduct them, what to include, and how to make this type of business reporting much easier to conduct.
- What is a Business Impact Analysis (BIA)?
- Why Is a Business Impact Analysis Important?
- How Often Should You Perform a Business Impact Analysis?
- Who Should Be Involved In the Business Impact Analysis?
- How Do You Define Business Impact?
- Types of Impact to a Business
- The 5 Areas of Business Impact Disruption
- Examples of Business Disruptions and Their Potential Impacts
- Business Impact Analysis vs. Risk Assessment: What Is the Difference?
- Business Impact Analysis vs. Project Risk Management: What Is the Difference?
- How Is Business Impact Calculated?
- How to Conduct a Business Impact Analysis?
- What Should Be Included in a BIA Report
- Business Impact Analysis Report Template
- Common Challenges With BIA Analysis and Reporting
- Improve Business Reporting with Databox
What is a Business Impact Analysis (BIA)?
A business impact analysis (BIA) is the process of predicting events that could be harmful to the well-being of your company and disrupt standard business operations. During this analysis, you gather data about your business functions, processes, and system so that you can prepare a continuance plan to mitigate the risks of disruption and minimize potentially huge losses.
For example, companies that conducted a BIA and prepared a continuance plan for a global pandemic scenario before Covid-19 occurred had an easier time prepping their employees to continue their work from home.
By running a business impact analysis, you can predict the consequences that specific disruptions can have on your business and create recovery strategies. In case the predictions come to life, you will be ready to act quickly and tackle the issues. Also, your team won’t be caught off-guard either since they will have a clear outline on how to respond to these specific changes.
In business impact analysis, there is a basic assumption that all components in an organization are co-dependent on one another. However, there are specific components that have much more value and require additional funding in case the unexpected happens. For instance, closing your cafeteria won’t have a huge impact on your business’s operations, but having your information system hacked can significantly damage the company.
Identifying vulnerabilities and gathering data for strategy development later results in a business impact analysis report which is used to describe the potential risks in detail.
Related: How to Write a Great Business Development Report: A Step By Step Guide with Examples
Why Is a Business Impact Analysis Important?
There is no company in the world that is immune to accidents, emergencies, or other unforeseeable events.
This is why it’s always better to be prepared to face the challenges as they emerge. By conducting BIAs frequently, you will have enough data to create efficient recovery strategies.
To be more specific, here are some particular things that make BIAs so important.
- Provides Confirmation of Business Continuity Program Scope
- Identifies Legal, Regulatory, and Contractual Obligations
- Provides Clarity on Business Continuity Strategy Spend
- Captures Preliminary Plan Content
Provides Confirmation of Business Continuity Program Scope
Business impact analysis provides you with an insight into which business resources and activities your company can’t go without. They are tied to the creation of the most significant products and services.
Once you understand the process behind these products and services, you can even uncover other resources that weren’t a part of the original program scope.
It is crucial to have a clear overview of which activities need to be performed and have the biggest impact on your program’s scope, no matter the circumstances.
Identifies Legal, Regulatory, and Contractual Obligations
Many stakeholders in the company often don’t have the clearest understanding of the legal, regulatory, and contractual obligations. Truth be told, it’s a rarity to find an organization that has a complete grasp of these obligations and understands the consequences of not fulfilling them.
By conducting BIAs, your team will be aware of the obligations and you can work together on creating a continuity plan to achieve compliance.
Provides Clarity on Business Continuity Strategy Spend
Figuring out how much you should spend on business continuity strategies is a very sensitive issue. But, BIA can shed some light on the matter.
Business impact analysis provides you with knowledge regarding the most important components that your organization needs in order to develop a sufficient business case. By using this knowledge, you will have an easier time identifying and implementing appropriate spending for continuity strategies.
Additionally, you will also have the needed data to justify the spending amount you set.
Related: How to Write a Great Business Expense Report: A Step-By-Step Guide with Examples
Captures Preliminary Plan Content
The business impact analysis is the first stage of the business continuity plans data collection process.
When the time comes to perform the BIA, your organization will start gathering plan contents like current controls, recovery strategies, team requirements, contract information, and other resource-related information that is needed to create a business continuity plan.
After you collect all of this information, you can provide the developers of the business continuity plan with a starting point so they don’t have to start from scratch with a blank template.
How Often Should You Perform a Business Impact Analysis?
Depending on the frequency of changes in your organization and the speed at which it evolves, business impact analysis should be conducted every one or two years.
However, if there aren’t many changes, businesses can perform them in even longer intervals. Conversely, if there are frequent changes, you should conduct them in shorter intervals.
Who Should Be Involved In the Business Impact Analysis?
The business impact analysis process requires a few different individuals and teams in order to be performed accordingly.
For determining the in-scope departments, the Business Continuity Steering Committee, Program manager, and Program Sponsor should all work together in this first step.
Next, an interviewer and a note-taker will be required during data gathering meetings. With the interviewer conducting the interview and the note-taker marking down key points, the process will be much faster. Subject matter experts and department team leaders should all be part of the interviews.
Finally, the Program Manager is the one who should present the BIA and risk assessment summary to the Business Continuity Steering Committee.
How Do You Define Business Impact?
Clearly defining a business impact can be a bit tricky, but here are a few tips that should help you do it.
For starters, a business impact is anything that changes the business’s current processes and operational activities. This can be any type of unforeseeable event.
However, we should note that not all business impacts are necessarily negative. There are plenty of events and activities that can transform the company to be more profitable and increase revenue.
In cases like this, the BIA report should also include the advantages that a certain impact has brought to the company.
On the other hand, we have business impacts that can have a negative effect on business operations. This is why it’s best to do the business impact analysis and recovery time assessment beforehand and buy your organization time to prepare for such events.
One of the most important things to know is which areas of your company would be affected by these events.
Will there be a data breach? A long-term power outage? Will you lose most of your clients? All of these questions need to be answered so you can create the best possible recovery strategy.
Types of Impact on a Business
Before you conduct a business impact analysis, you are going to need to create an operational impact assessment template.
Here are some different types of business impacts that you can include in the template:
- Sudden expansions
- Major downsizing
- Acquisitions or mergers
- New technology implementation
- Natural disasters
- Sudden building/infrastructure damages
- Equipment/machinery malfunctions
- Data security breaches
- Global pandemic
- Cyber attacks
- Theft
- Product line modifications
- Interruptions in the supply chain
The 5 Areas of Business Impact Disruption
While there are plenty of different components in an organization, they are not all equally important. In each business, there are five key areas that, if disrupted, could bring an avalanche of problems.
Recognizing these areas will help you create your risk mitigation strategies to revolve around them and minimize the impact of disruption. It’s essential that you have a full understanding of what these areas include.
The five core areas of business impact disruption are:
Technology
The ‘Technology’ area captures all parts of your tech infrastructure that could be affected by unexpected events.
For instance, if your company has to upgrade to new software for day-to-day activities, this change can fall under the ‘technology’ area.
The things you should examine during a BIA for technology infrastructure are approximate downtime during upgrades, how long would a backend implementation take, and how would the employees be affected.
People
As the old saying goes, “Your people are your most important asset in the company”.
Figuring out how an unexpected event could impact your people and the work that they do is essential in any good business impact analysis.
Business changes and operational disruptions typically require your employees to become familiar with new processes, learn how to react in a crisis, or how to adopt new workflows.
For example, the Covid-19 pandemic required some huge adjustments in terms of remote working accommodations.
In your BIA template, you should consider how certain changes can impact the employees, managers, vendors, customers, and any other essential people within the business.
Process & Policy
The ‘Process & Policy’ area refers to any changes that have to be made to the standard firm policies.
Let’s say that you have created a new rule that all of your employees must provide additional IDs when entering the building. You would have to update the company’s procedures and policies. Also, you will need to come up with solutions for situations where the employees have forgotten the IDs.
These types of events are considered a process & policy disruption and they should be included in the business impact analysis.
Organization
Organizational disruptions are the most critical and can bring huge losses.
This impact category should capture all the possible disruptions in the organization, from mergers/acquisitions to company downsizings due to economic reasons.
Business Strategy
Events that impact the strategies implemented in your company should be placed in the ‘Business Strategy’ area of your business impact analysis template.
Sometimes, it can be difficult to differentiate business strategy impacts from organizational impacts. For example, let’s say that you are planning to change your product line so you can focus more on sustainability. This wouldn’t require any specific organizational changes but you would need to implement a new business strategy.
Examples of Business Disruptions and Their Potential Impacts
While there are plenty of scenarios that all organizations should consider, it’s also important to be able to differentiate business disruptions and business impacts.
Business disruptions include:
- Natural disasters
- Hacking attempts and data security breaches
- Key employee departures
- Key supplier departures
- Damaged equipment
- Utility/Power outages
- Delays in schedule
Business impacts include:
- Customer departures
- Postponing business plans due to disruptions
- Unexpected expenses
- Delayed payments
- Losses in sales or revenue
- Legal penalties
Business Impact Analysis vs. Risk Assessment: What Is the Difference?
Business impact analysis and risk assessment reports have a lot of similarities, but there are some crucial things that separate them.
The main difference between these two is that risk assessment is used for analyzing potential threats and estimating how likely they are to occur.
On the other hand, business impact analysis is used for determining how those threats would impact the standard operations and activities with the company.
To put it simply, business impact analysis goes one step further than risk assessment reports and measures the severity of the potential threats.
Business Impact Analysis vs. Project Risk Management: What Is the Difference?
Project risk management refers to recognizing, analyzing, and preventing potential risks that could have an impact on the company’s projects. Essentially, anything that could affect the project (delaying the timeline, project failure, reduced performance, etc.) should be included in a project risk management report.
In project risk management reports, the main focus is identifying the potential risks to specific projects, while a business impact analysis measures things on a larger scale.
There isn’t one specific project that is analyzed by BIAs – it’s all the business functions, activities, processes, and operations within the company that are under the loop.
How Is Business Impact Calculated?
When calculating the impact that a potential disruption could have on your business, your BIA report should answer these questions:
- How severe would the impact be?
- What would be the scope of the impact?
- Will I be able to use alternative processes if the key ones are disrupted?
- How much time would we need to recover from this disruption?
- How many processes within the company need to be changed?
- What is the exact amount of people that would be affected?
- Will there be any necessary changes to job roles?
- What would be the monetary losses?
To calculate a business impact, you should come up with rough estimates for all of these questions.
PRO TIP: Are You Tracking the Right Metrics for Your SaaS Company?
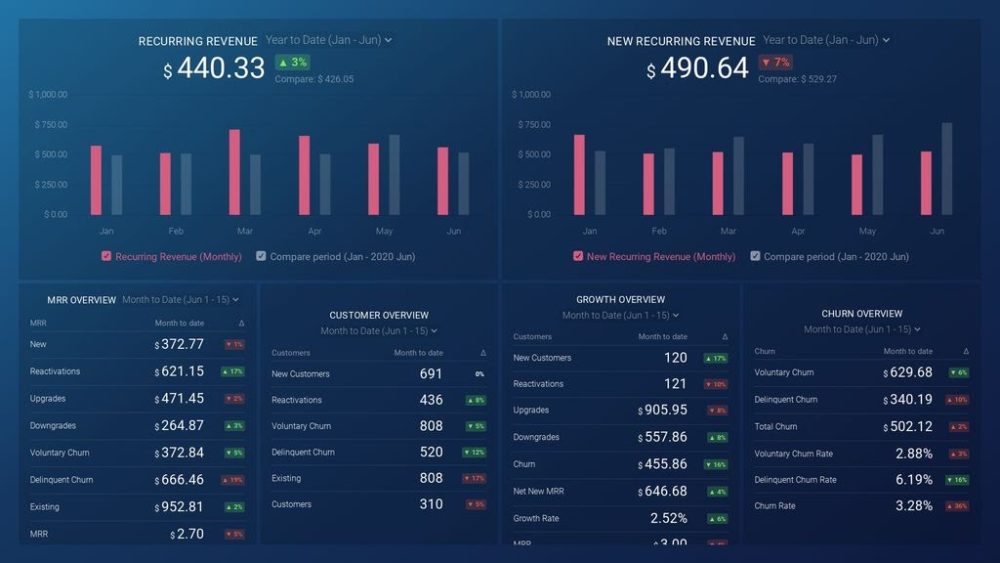
As a SaaS business leader, there’s no shortage of metrics you could be monitoring, but the real question is, which metrics should you be paying most attention to? To monitor the health of your SaaS business, you want to identify any obstacles to growth and determine which elements of your growth strategy require improvements. To do that, you can track the following key metrics in a convenient dashboard with data from Profitwell:
- Recurring Revenue. See the portion of your company’s revenue that is expected to grow month-over-month.
- MRR overview. View the different contributions to and losses from MRR from different kinds of customer engagements.
- Customer overview. View the total number of clients your company has at any given point in time and the gains and losses from different customer transactions.
- Growth Overview. Summarize all of the different kinds of customer transactions and their impact on revenue growth.
- Churn overview. Measure the number and percentage of customers or subscribers you lost during a given time period.
If you want to track these in ProfitWell, you can do it easily by building a plug-and-play dashboard that takes your customer data from ProfitWell and automatically visualizes the right metrics to allow you to monitor your SaaS revenue performance at a glance.
You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your Profitwell account with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
How to Conduct a Business Impact Analysis?
If conducting a business impact analysis seems like a grueling process – it’s because it is.
BIA reporting is one of the most difficult and time-consuming types of business reporting. You will have to gather a wealthy amount of data, predict ‘unforeseeable’ events, measure how they will impact your business, and then come up with a recovery strategy in case these events do take place.
While there is no universal way to conduct BIAs, we have prepared a few steps that could be applied in any business to make the process a bit easier.
- Proper Planning: Scope the Business Impact Analysis
- Gathering Information: Schedule Business Impact Analysis Interviews
- Analyze the Data Gathered: Execute BIA and Risk Assessment Interviews
- Write the Report: Document and Approve Each Department-Level BIA Report
- Complete a BIA and Risk Assessment Summary
Proper Planning: Scope the Business Impact Analysis
You should think of business impact analysis just as any other significant project in the company.
Firstly, you will want to create a project outline that includes the overall goals of the BIA, scope analysis, and specific shareholders that you will be working with. By having all of this information in writing, your shareholders will have an easier time coordinating the resources you need.
Also, you should make sure to organize the significant components of the business impact analysis so your team can easily understand which information and data they need to gather.
To be sure all the important activities and resources are in-scope, you can also organize frame meetings. Frame meetings are used for addressing certain questions such as:
- What is the purpose of the business continuity plan?
- What products/services will try to protect?
- Who are the parties that will be involved in the program?
- How much business continuity is enough?
These types of meetings can greatly benefit your business continuity program. You will be able to clearly outline which team is responsible for which program objectives, decide the participants of the program, and figure out the most important in-scope products and services that should be included in the continuity program.
By identifying these products and services, you will come up with strategies aimed to maintain the operations needed for their production.
A good business impact analysis will clearly outline the tasks each department has in order to deliver the primary products and services.
Gathering Information: Schedule Business Impact Analysis Interviews
Before you try to figure out what outcomes can come from certain disruptions, you will first have to gather information regarding the most important processes in your business. For this, you are going to need help from the stakeholders who are managing these core areas.
You might already have an overview of these processes and understand the big picture, but you will need some additional information from the people closest to the work.
By talking to the people who are ‘in the trenches,’ you will have an easier time coming up with efficient solutions and strategies.
For gathering data, it’s best to:
- Conduct individual interviews with the stakeholders
- Organize a BIA questionnaire
The best method is to use the ‘hybrid approach’. Conduct interviews, but also organize questionnaires that the participants should answer afterward.
When picking which shareholders to talk to, you should make sure that they:
- Understand the core areas of the organization (related to products/service)
- Understand the standard everyday activities and processes that their departments complete
- Understand how much resources are necessary for the completion of these activities
Related: The Most Valuable Customer Service Interview Questions for Gathering Customer Feedback
Analyze the Data Gathered: Execute BIA and Risk Assessment Interviews
Once you have all the essential data regarding the business activities and processes, you can move on to the analysis.
For gaining better insight, you will need answers to these questions:
- Which are the crucial processes needed for maintaining standard business operations? Start by coming up with a list of prioritized functions. This way, even if the worst case scenario does happen, you will have an idea which processes have to be revitalized first.
- What resources do the processes require in order to operate? The answer could be anything from employees and technology to raw materials and other physical resources. When you understand which resources are the most important, you can prioritize them during the impacts.
- How much time and money will you need to get the processes up and running again? Make rough estimates regarding the timeline and budget of your recovery strategy. This way, you will be prepared to face certain losses and will minimize the time you need to get things back on track.
To simplify, you will need to figure out the dependencies needed for each activity to function properly.
You can document dependency types by using this categorization:
- Vendors
- Staff
- Equipment
- Business facilities
- Applications
- Additional departments
Next to each of these dependencies, you should describe why they are used, who are the suppliers, what would be the recovery time, and what are the key recovery objectives.
When conducting the risk assessment interview with the stakeholders, ask them how likely would it be for a certain dependency to be impacted on a scale from 1-10.
After doing the interviews, you can multiply the numbers to calculate the risk rate for each dependency.
Also, it can be useful to pull out data about historical impacts that have disrupted the operational activities in the past, so you know which carry the highest risks.
Related: How to Analyze Data: 30+ Experts on Making Sense of Your Performance
Write the Report: Document and Approve Each Department-Level BIA Report
After completing the analysis process, you can move on to creating separate department-level BIA reports.
When the department-level meetings come to an end, you will need the information and results documented in separate reports.
A department-level BIA report should include all the key data and information that was acquired during the interview, along with specific data-based suggestions.
Keep in mind, simply conducting a business impact analysis isn’t enough. The report that comes out of it is the most important part of the whole process. You will use it to convey the information and findings to the highest-ranking members of the company and help them understand the continuance plan. If needed, they will make certain changes and later approve the document.
Later, you will use the department-level reports and combine them to create one comprehensive BIA report that captures all the core areas.
Complete a BIA and Risk Assessment Summary
Once you wrap up the department-level reports and they have been approved by the internal stakeholders, you should start creating a comprehensive BIA and risk assessment summary.
These summaries should include a complete overview of the most significant activities, required resources, and risks that were uncovered during department-level interviews.
The reports are used as a foundation for making efficient strategies that could be a response to the risks you have identified.
When you start presenting the BIA and risk assessment results to your stakeholders, your main focus should be on:
- Highlighting the key products and services of the business
- Establish a rough estimate for recovery and how it aligns with products/services
- Explain the biggest risks and provide strategies on how to react to them
What Should Be Included in a BIA Report?
Now that you know what a business impact analysis is and how you should conduct it, we can move on to the necessary components of the BIA reporting process.
A business analysis impact report helps you and other high-ranking members of the company to create recovery plans based on the information you gathered.
Creating a BIA report is the most important part of the process since it directly conveys your finding to the leadership and allows all of you to come up with the right continuity plan in case of disruptions.
Of course, BIA reports will be different in every company, but these are some of the universal things that should be included.
These include:
- Executive summary
- Objectives and scope
- Methodology
- Summary of your findings
- Breakdown of your findings for each process
- Supporting documents
- Recommendations for recovery
Executive summary
An executive summary is an essential part of the BIA report since it allows the stakeholders to gain insight into what the report includes even if they don’t have enough time to go through the entire document.
This section of the report should include:
- The extent of the BIA analysis – Which organization components were analyzed?
- Main goals – Which are the primary objectives you identified during the business impact analysis?
- Overall BIA approach – The whole process that led to the creation of the report.
You can also create an executive summary template to help you repeat the process in different reports.
Objectives and scope
In this section of the report, you should go into detail about the key objectives of your business impact analysis and explain why they are so significant.
Next, add information regarding the scope of the analysis. This is essentially the subset of data that you have used for analysis.
Related: Goals Based Reporting: Everything You Need to Know
Methodology
The methodology section should describe how you conducted the business impact analysis.
This includes information such as:
- The interview process
- How did you analyze the data
- Which assumptions did you make
- What quantitative categories did you use to measure the impact (explain their meanings and rank them)
Summary of your findings
You can create this section by presenting the most important information of each finding. Make sure you include all the significant data so your stakeholders can grasp the bigger picture without having to go through each finding separately.
A good idea might be to create a table of findings so you can categorize the information easier and make it more understandable for the readers.
Breakdown of your findings for each process
This will probably be one of the longer sections in your business report and you will want to make it as comprehensive as possible.
The things you should include in this section are:
- List of the most important business processes – Specify which business processes and activities in your company are most important and, if possible, rank them.
- Impact of potential disruptions on those processes and different areas of your business – Explain how certain events can disrupt the key business processes and which areas will be affected.
- Recovery time objective (RTO) – Make a rough estimate of how long your business could tolerate the consequences of the disruptions.
- Recovery point objective (RPO) – What amount of losses would your company be able to tolerate?
- A comparison between the potential financial cost of disruption and the cost of business recovery strategies – It’s important to include how much money a disruption would cost your business and how much you would have to spend to implement the recovery strategy. Make a comparison of the two to see if the strategy would be able to cover the losses.
Supporting documents
Some of your shareholders might be interested in checking out the details of the BIA process, participant names, IT system recovery time, or any other specifics.
All of this should be placed in the ‘Supporting Documents’ section.
Recommendations for recovery
This will be one of the last sections of your report, so make sure you combine the data you presented and add a summary through which you explain what will be required to keep the business operational.
Make several recommendations for recovery and discuss them with your internal stakeholders.
Business Impact Analysis Report Template
Based on all of the sections that we talked about in the last heading, here is a BIA report template that you can use to make the reporting process a bit easier.
- Executive summary
- Objectives and scope
- Methodology
- Summary of your findings
- Breakdown of your findings for each process (need to include the following)
- List of the most important business processes
- impact of potential disruptions on those processes and different areas of your business
- Recovery time objective (RTO)
- Recovery point objective (RPO)
- A comparison between the potential financial cost of a disruption and the cost of business recovery strategies
- Supporting documents
- Recommendations for recovery
Common Challenges with BIA Analysis and Reporting
When conducting a BIA analysis, you are inevitably going to run into certain challenges. Considering that BIA reporting is one of the most tedious business reporting processes, this comes as no surprise.
Here are some of the most common challenges with BIA analysis and reporting, and a few tips on how to overcome them.
- The BIA Is Time-Consuming
- Inaccurate or Unrealistic Recovery Time Objectives (RTO)
- The BIA Doesn’t Evolve as the Organization Evolves
- BIA Data Is Overwhelming to Analyze
- BIA Data is Useless or Irrelevant
- Disengaged Executives
The BIA Is Time-Consuming
In most companies, the BIA is considered a grueling process and it leaves you with little to no time to deal with your other priorities.
You will spend hours gathering the data, days interviewing the participants, and then spend a hefty amount of time analyzing all of the findings.
The main root of this problem is that most companies still do business impact analysis reporting manually.
To make the BIA less time-consuming and save time for other value-bringing activities, the best advice is to switch to business intelligence tools such as Databox.
Databox allows you to quickly gather all the data you need and connect it to one comprehensive report where you can later do the analysis. You can also update the information in real-time and save both time and nerves.
Related: How Deeplite Saves Time and Optimizes Spend in Real-Time with Databox
Inaccurate or Unrealistic Recovery Time Objectives (RTO)
Recovery time objectives (RTO) are an indispensable part of BIA reports. You will have to identify which business activities and processes are the most important, set goals, and specify recovery time objectives.
RTOs help your team gain an insight into which activities are the most time-sensitive and how long your company could tolerate the disruptions.
The main problem with RTOs is assigning them without sufficient business justification. Make it a priority to ask team leaders about their opinions on the department’s capabilities and draw conclusions and suggestions based on that.
The BIA Doesn’t Evolve as the Organization Evolves
A business impact analysis isn’t a one-time thing. As your business changes and develops, the BIA has to be updated as well.
Make sure you conduct business impact analysis frequently or as soon as changes occur within the company. This way, you will be able to stay on top of your recovery strategies and be more prepared in case disruptive events do impact your business.
BIA Data Is Overwhelming to Analyze
If the data in your BIA report seems too overwhelming to analyze, you might have a problem with incorrect scoping.
There are two main questions that you have to answer:
- Which are the primary business activities that affect standard operations and allow the company to meet its overall objectives and legal obligations?
- How long can you go without these activities and resources before the business suffers irreversible losses?
Many BIA practitioners make the mistake of using organizational charts and facility lists to find the information they need for the BIA report. This may seem logical at first, but you will end up with way too much data that will require twice the time to analyze.
The best scoping method involves figuring out the main products and services, organizational outputs, and then conducting interviews with team leaders regarding their part in the delivery of these products.
This way, you will only acquire the data relevant to your report and make the analysis process much easier.
BIA Data is Useless or Irrelevant
There are two reasons why data may seem useless or irrelevant:
- You haven’t done a good job finding the right BIA participants
- Your data gathering methods aren’t efficient
Incorrectly Identified BIA Participants
When picking the participants of your BIA analysis, you have to find subject matter experts (SME) that are the closest to the work done in a department and know how they contribute to the delivery of products and services.
By speaking only to the shareholders and executives, you won’t get much important information regarding the day-to-day activities since they will prioritize other tasks in the company.
This also applies to low-level employees that don’t have enough insight into the overall organizational process and can’t grasp the bigger picture.
The best way to identify the right BIA participants is by asking these questions:
- Does the participant have enough knowledge regarding the department’s role and contribution to the delivery of key products and services?
- Does the participant know which resources are required for the standard operations to continue?
- Is the participant familiar with activity inputs, activity outputs, dependencies, and other departmental activities?
Ineffective Data Gathering Methods
Choosing the wrong data gathering methods can also lead to ‘irrelevant’ BIA data.
Assuming that a BIA process only requires several surveys is a costly mistake. Even though surveys are the quickest and most effortless way to gather data from department leaders, they don’t provide the same amount of business continuity awareness as other methods do.
The most effective way to gather data is by conducting the interviews in person. This way, you collect consistent information and you can ask the interviewees to clarify certain information that may come off as confusing.
Also, you can even consider using a hybrid approach where you give the interviewees questionnaires to complete before or after the interview.
Related: 8 Common Mistakes in Data Analysis for Marketers to Avoid
Disengaged Executives
To make sure your company is prepared and your recovery strategy is solid in case disruptive events take their toll, you will need help from your high-level executives.
Their involvement is key for providing efficient strategy directions and organizational resource allocation. If you fail to keep the executives engaged through your report, your business continuity program won’t be of much use and your company won’t be prepared for business impacts.
To make sure they understand the importance of the BIA process, you can include team leaders and Business Continuity Steering Committee members to participate in your BIA report presentation.
The main pain points you want your high-level executives to understand are:
- Key business activities and which departments support them
- Most valuable products and services
- Recovery expectations
- Impact areas
- BIA participants
It’s best to also include a detailed executive summary that covers all of these points in an understandable manner.
The things you should avoid are:
- Non-strategic conclusions
- BIA outcomes with no business justification
- Providing a pile of data that they will need to analyze themselves
Improve Business Reporting with Databox
Business impact analysis reporting is important for many reasons. It allows you to create recovery strategies and continuance plans that you can implement in case of any severe business impacts. If any disruptive events do occur, you and your team will be ready to face the challenges head-on and get your standard operations up and running in no time.
While the trend of ‘neglecting’ the importance of BIA reports grew significantly in the past few years, the global pandemic that struck the world in 2020 reminded us just how significant these business reports are.
However, as important as they may be, creating BIA reports is an extremely daunting task that will take up both your time and nerves. That is, if you do it manually.
Databox can help you turn this around.
Advanced business intelligence like Databox can make the whole process much simpler and it will help you save up valuable time.
By using our customizable dashboards, you can connect all the data you gather from interviews and questionnaires into one comprehensive report. Once you have that large pile of data in one place, you will also have an easier time analyzing it and drawing conclusions afterward.
Additionally, you can also combat the ‘boringness’ of BIA reports by using our beautiful visualizing features like graphs and charts to make the information much more presentable and understandable to your stakeholders. Best of all, you can do it in only a few clicks of a button.
Sounds impressive? Sign up for a free trial today and experience the magic of Databox first-hand.